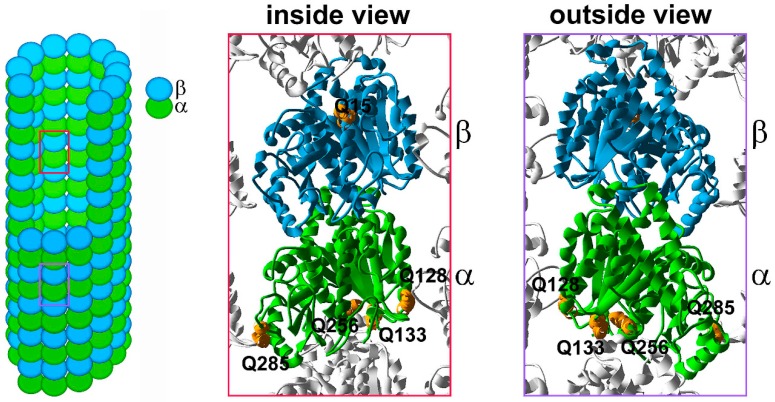
Figure 1.
The distribution of the polyamination sites in α,β-tubulin heterodimer. Schematic representation of a microtubule, composed of α- (green) and β- (blue) tubulin heterodimers. Red and purple frames mark tubulin heterodimer with either a visible luminal side (an inside view) or outer surface (outside view), respectively. An inside and outside views of 3D model of the tubulin heterodimer within the microtubule lattice based on 3J6F.pdb (NCBI database); a tubulin molecule is composed of 12 α-helices (numbered H1–H12) and 10 β-strands (numbered S1–S10) linked by loops [8,9]. Putative tubulin polyamination sites are marked in orange. α-Tubulin Q128 is located within the H3–S4 loop and builds the H3 surface, which is involved in lateral interactions with the neighboring protofilament (an outside view, protofilament to the left). α-Tubulin Q285 is located within the S7–H9 loop, the so-called M loop, which is also responsible for lateral interactions with the neighboring protofilament (an outside view, protofilament to the right). α-Tubulin Q133, located within the H3–S4 loop and Q256 located within the H8 helix, build the minus end surface, responsible for longitudinal interactions between heterodimers within the same protofilaments or with γ-tubulin at the nucleation site. Q15 of β-tubulin is located within the H1 helix, positioned near the nucleotide binding pocket.