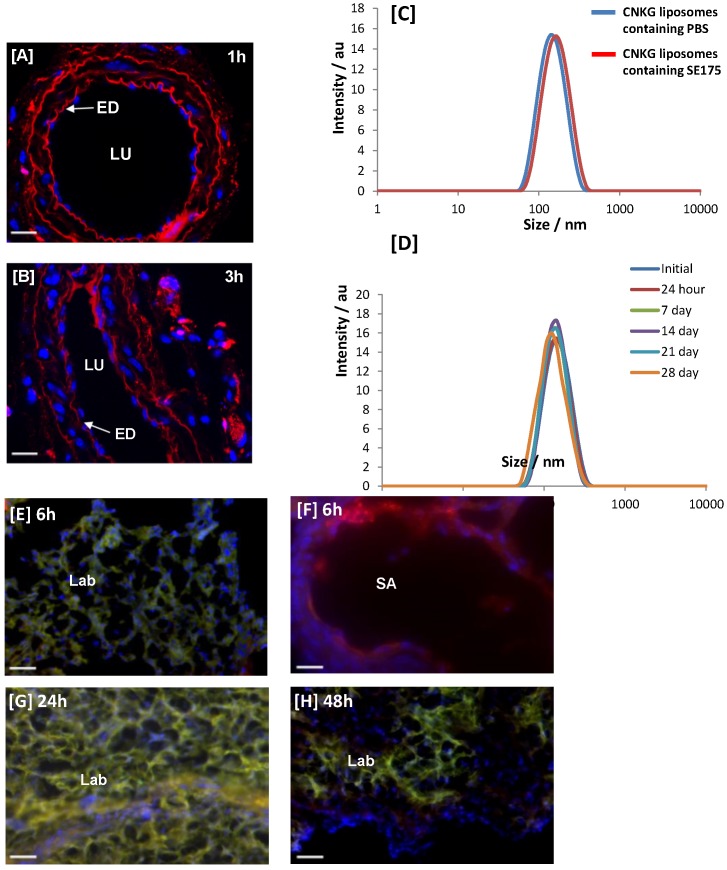
Figure 2.
CNKGLRNK binding to uteroplacental tissue in vitro and in vivo [A, B] Segments of mouse uterine artery were incubated with Rh-CNKGLRNK (0.27 µmol/L; red) for up to 3 h. Peptide binding and uptake was assessed by fluorescence microscopy (n = 3). Representative images are shown. Rh-labelled peptides, red; DAPI (nuclei), blue. ED = endothelium; LU = lumen. Scale bar = 50 µm. [C] Size distribution of freshly prepared Rh-CNKGLRNK-decorated liposomes containing either PBS (blue) or SE175 (red). A representative plot from n = 3 liposome preparations is shown. [D] Size distribution of Rh-CNKGLRNK-decorated liposomes containing PBS over a 28 day period (n=3). Representative plots from one preparation are shown. [E - H] Placentas from pregnant C57BL/6J mice collected at E18.5, following tail vein injection of Rh-CNKGLRNK (red)-decorated liposomes composed of NBD-labelled lipids (green), 6h, 24h or 48h prior to tissue harvest. Cardiac perfusion was performed to remove unbound peptide; organs were removed and assessed by fluorescence microscopy. Yellow, co-localisation of peptide (red) and lipid (green) fluorescence. Blue, DAPI (nuclei). SA, spiral artery; LB, labyrinth. Scale bars = 50 µm. n = 3 placentas from n = 3 mice per treatment group were examined. Representative images are shown.