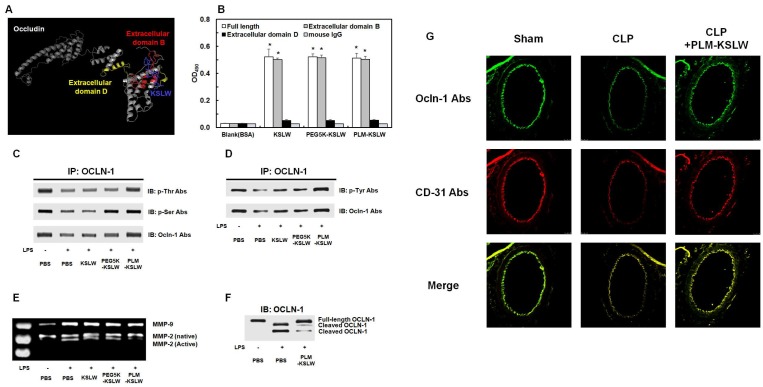
Figure 3.
Binding affinities of KSLW, PEG-KSLW, and PLM-KSLW toward OCLN and their effects on the cleavage of OCLN. (A) Binding of KSLW (blue) to the extracellular domain B (red), extracellular domain D (yellow), or other sites (gray) of OCLN was predicted using the ZDOCK server. (B) The ability of KSLW, PEG-KSLW, and PLM-KSLW to bind to full-length OCLN (white), extracellular domain B of OCLN (gray), or extracellular domain D of OCLN (black) were measured by performing ELISA; *p < 0.05 vs. BSA (B). All results are expressed as mean ± SD of three independent experiments performed on different days. (C and D) PLM-KSLW suppressed LPS-induced phosphorylation of Thr, Ser, and Tyr residues of OCLN, as determined by performing immunoprecipitation (IP) and immunoblotting (IB). (E) Enzymatic activity of MMP-2 or MMP-9 in cell culture supernatants of LPS-treated HUVECs was determined by performing SDS-PAGE gelatin zymography. (F) Protective effect of PLM-KSLW against the cleavage of OCLN in HUVECs treated with LPS (1 μg/ml, 12 h) was determined by performing western blotting. (G) Protective effect of PLM-KSLW on the cleavage of OCLN after CLP was examined by performing immunohistochemistry. OCLN (green) and CD31 (red) were stained with the respective fluorescent antibodies and were imaged by performing confocal microscopy. Images are representative of three independent experiments.