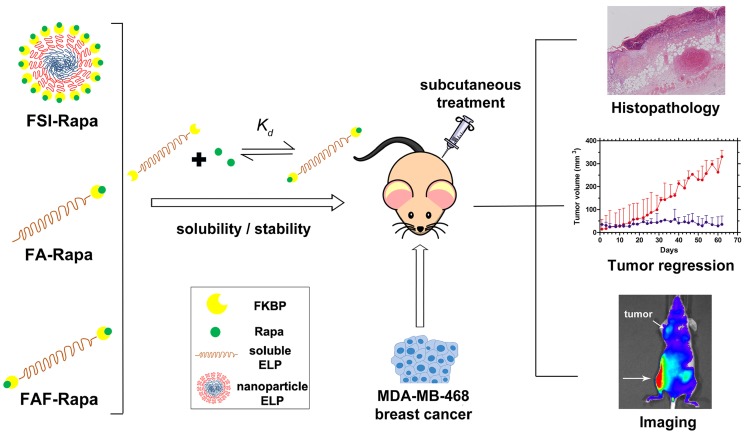
Figure 1.
Optimization of FKBP-ELP architecture to enhance the stability and efficacy of Rapa delivery. Rapalogues are potent cytostatic molecules with anti-cancer efficacy; however, their poor solubility limits their safety and efficacy by oral and IV delivery. This manuscript describes a new protein-based strategy to deliver Rapa via SC delivery using fusions between the FKBP protein and ELP (Table 1). This side-by-side comparison evaluates soluble ELPs with one (FA) or two (FAF) drug binding domains with a nanoparticle ELP (FSI). While all three carriers can bind Rapa, reduce injection site toxicity, and suppress a human breast cancer xenograft (MDA-MB-468), the Berunda polypeptide named FAF performed best with respect to drug loading, drug retention, formulation stability, tumor efficacy and bio-distribution following SC administration.