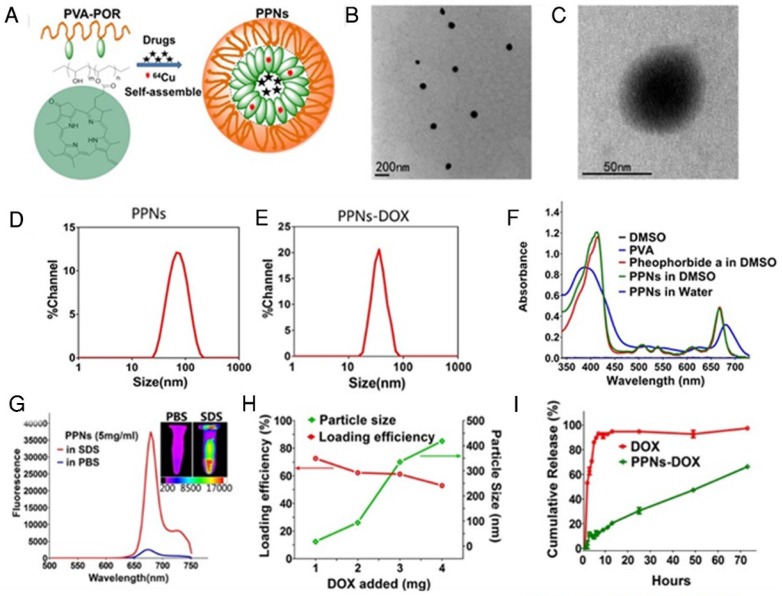
Figure 1.
The schematic illustration of fabrication of PPNs by one-pot approach and characterizations of the resulting PPNs. (A) Schematic representation of PPNs prepared by the self-assembly of PVA-porphyrin conjugates. (B, C) TEM images of PPNs stained with phosphotungstic acid. (D, E) Size distribution of PPNs and DOX-loaded PPNs (PPNs-DOX, DOX initial loading at 1mg/20mg PPNs) in PBS, measured by dynamic light scattering (DLS). (F) Absorption spectra of PVA (blue), pyropheophorbide a (red) and PVA-porphyrin conjugates (green) in DMSO & water. (G) Fluorescence emission spectra of PPNs in PBS (blue) versus dissociated state of PPNs in the presence of SDS (red), as well as near-infrared imaging of PPNs solutions in PBS and SDS, respectively. (H) The DOX loading efficiency of PPNs and the particle size change of PPNs-DOX versus the level of drug added at initial loading. The amount of DOX was varied from 1 to 4 mg while that of PVA-porphyrin was kept at 20mg. PPNs-DOX with initial loading at 1mg/20mg PPNs were used for the following in vitro and in vivo studies. (I) Cumulative DOX release profiles from free DOX and DOX-loaded PPNs by dialysis method.