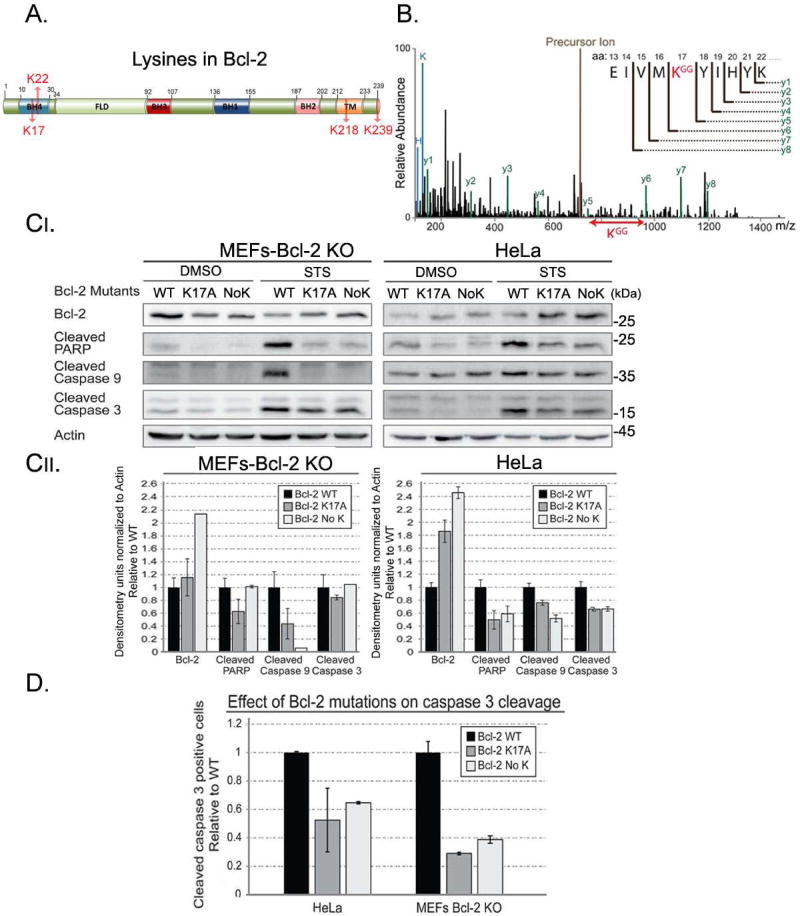
Figure 7. Lysine 17 (K17) is the main ubiquitin acceptor in Bcl-2.
A. Schematic representation of Bcl-2 highlighting its four lysine residues. B. MS/MS spectrum spanning the ubiquitylation site in Bcl-2. The trypsin cleaved peptides were enriched for Gly-Gly peptides using Pilot Ubiquitin Remnant Motif (K-ε-GG) kit and subjected to liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry separation. Precursor ion (brown) represents the uncleaved GFP-Bcl-2. Lines represent the relative abundance of detected peptides. The lines in black represent peptides that are not cleaved products of the precursor ion (y1–y6) and precursor ion of the un-fragmented peptide (brown). Lines in green (y1–y8) represent the cleaved GFP-Bcl-2 peptides and their corresponding amino acid sequence. KGG (red) represents an ubiquitylated lysine. This analysis identified Lysine 17 in Bcl-2 as the acceptor for XIAP-mediated ubiquitylation. C. MEFs Bcl-2 KO and HeLa cells were transfected with expression vectors for WT Bcl-2 (WT), Bcl-2 containing a substitution mutation of Lysine 17 into Alanine (K17A), and Bcl-2 in which all Lysines were changed to Alanine (No K). Increased levels of mutant Bcl-2 (K17A, No K) were seen upon apoptotic induction. This was accompanied by a decrease in apoptosis, as shown with three different apoptotic markers. Densitometry analyses are shown in the lower panel. D. Bcl-2 KO MEFs and HeLa cells were transfected with Bcl-2 as in (C) together with a GFP-cleaved caspase-3 reporter. Bcl-2 KO MEFs and HeLa cells expressing lysine mutants had significantly less cleaved caspase 3-positive cells compared to WT Bcl-2. These results suggest that Lysine 17 is the main acceptor for ubiquitylation of Bcl-2.