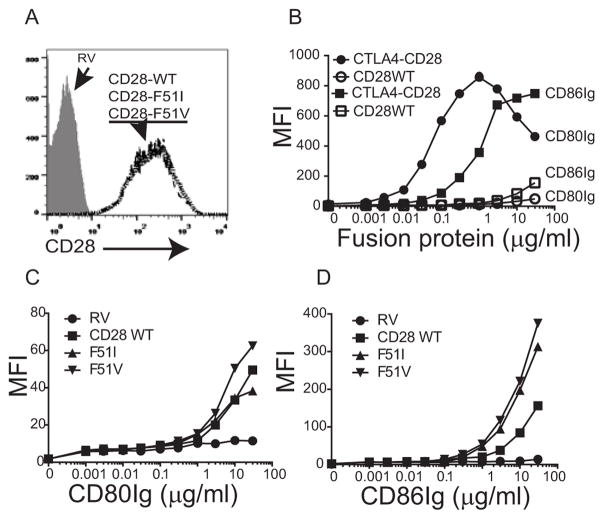
Figure 3. CD28 mutations enhance binding to CD80 and CD86.
A) Retrovirally transduced CD28-deficient splenocytes were stained with fluorescently conjugated anti-CD28 antibody and the GFP positive cells assessed for CD28 expression by flow cytometry. The histograms for WT and mutants are shown as overlays and are superimposable. B–D) CD28-deficient splenocytes were transduced with either empty vector (RV), wild type CD28, the CTLA4-CD28 chimera (panel B), or the CD28-F51I or F51V mutant constructs (panels C and D) and incubated with human CD80Ig or CD86Ig at the indicated concentrations followed by a fluorescently conjugated anti-Ig antibody. Binding was assessed by flow cytometry.