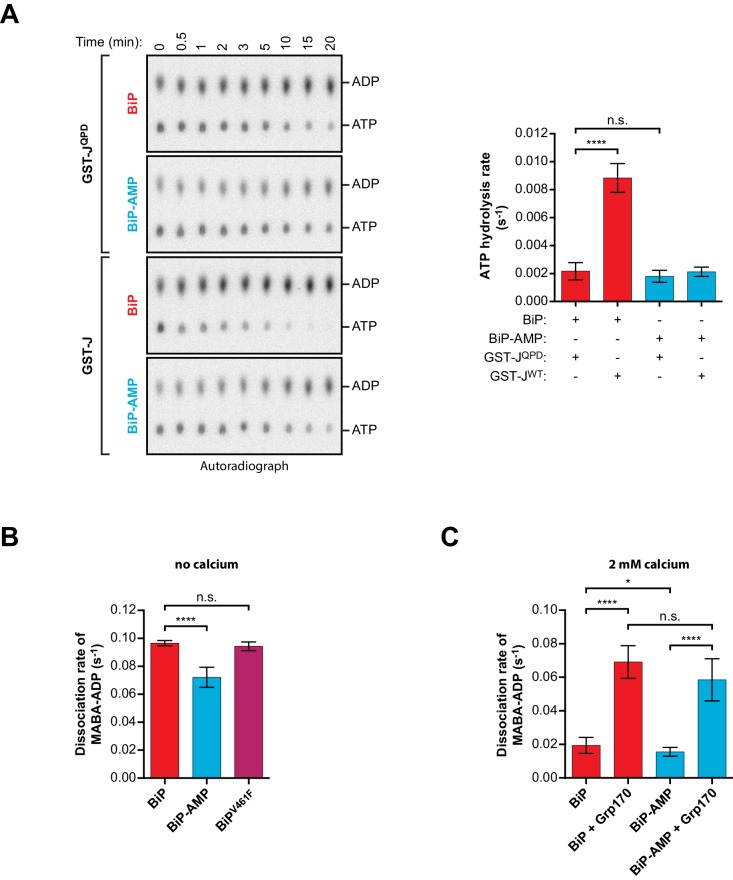
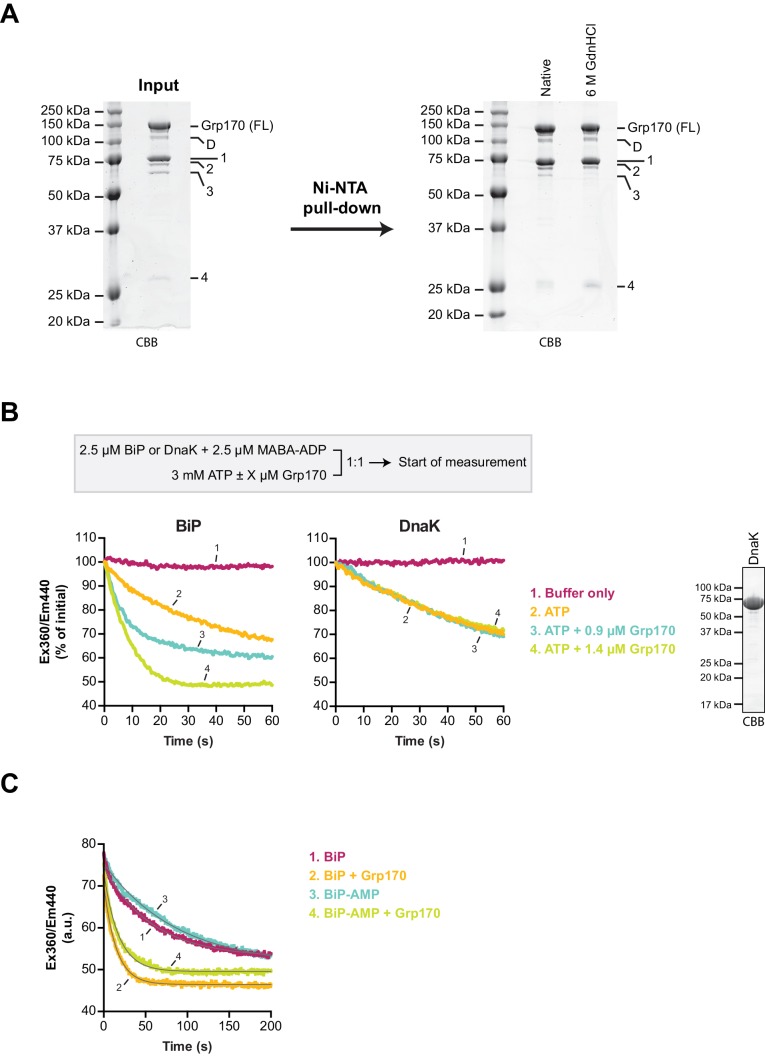
Figure 6. Effect of AMPylation on J domain-stimulated ATPase activity of BiP and ADP release from BiP.
(A) Shown is an autoradiograph of 32P-labeled ATP and ADP separated by thin-layer chromatography, the products of a single-turnover ATPase assay to analyze the effect of AMPylation on ATP hydrolysis by BiP. Pre-formed complexes between purified unmodified or AMPylated wildtype BiP protein and α-32P-ATP were incubated without or with wildtype GST-J or the QPD mutant for the indicated times prior analysis by thin-layer chromatography. A representative experiment is shown on the left and the signals from five repeats of the experiment were quantified and the calculated ATP hydrolysis rates are presented on the graph. Error bars represent standard deviations. ****p<0.0001, n.s. p>0.05. (B) Measurement of nucleotide release from BiP in absence of calcium. Unmodified or AMPylated wildtype or V461F mutant BiP proteins were incubated with the fluorescent ADP derivative MABA-ADP and the dissociation of the formed complexes was measured upon dilution with a solution containing excess of ATP to prevent re-binding of MABA-ADP. The dissociation rates of at least three independent repeats are shown. Error bars represent standard deviations. ****p<0.0001, n.s. p>0.05. (C) A similar experiment as in ‘B’ was performed in presence of 2 mM calcium in the solution and without or with Grp170. The dissociation rates of at least five independent repeats are shown. Error bars represent standard deviations. *p=0.0281, ****p<0.0001, n.s. p>0.05.