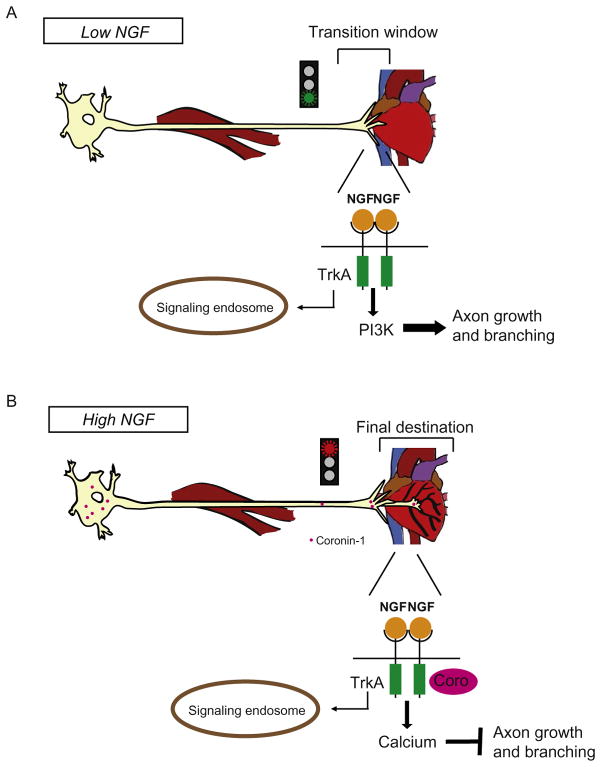
Fig. 4.
(A) Upon initially encountering a target organ, NGF concentrations are low and NGF-induced genes are not yet expressed. This marks a “transition window,” in which low NGF availability enhances axon growth and branching via PI3K signaling. (B) High NGF induces Coronin-1a expression, and PI3K signaling is dampened. Axon growth and branching slows.