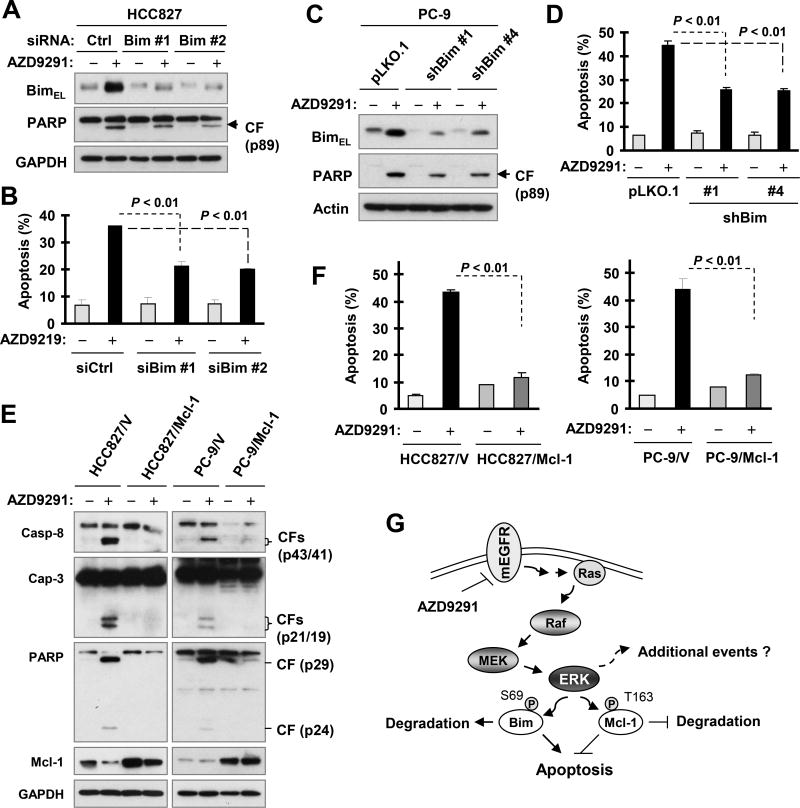
Fig. 3. Blockage of Bim elevation (A–D) or enforced expression of ectopic Mcl-1 (E and F) protects cancer cells from undergoing apoptosis induced by AZD9291, thus demonstrating a critical role of Bim and Mcl-1 modulation in mediating AZD9291-induced apoptosis in mutant EGFR NSCLC cells (G).
A and B, HCC827 cells were transfected with the indicated siRNAs for 48 h and then exposed to 100 nM AZD9291 for an additional 24 h. Bim knockdown and PARP cleavage were detected by Western blotting (A) and apoptosis was measured by annexin V/flow cytometry (B). C–F, The indicated stable transfectants were exposed to 100 nM AZD9291 for 24 h and then harvested for annexin V staining followed by flow cytometric analysis to detect apoptosis (D and F) and for Western blotting to detect the indicated proteins (C and E). The data are means ± SDs of duplicate (B, D and F) determinations. G, A schematic working model for induction of apoptosis by AZD9291 in mutant EGFR (mEGFR) NSCLC cells through modulating ERK-dependent degradation of Bim and Mcl-1 as well as yet-to-be identified additional mechanisms.