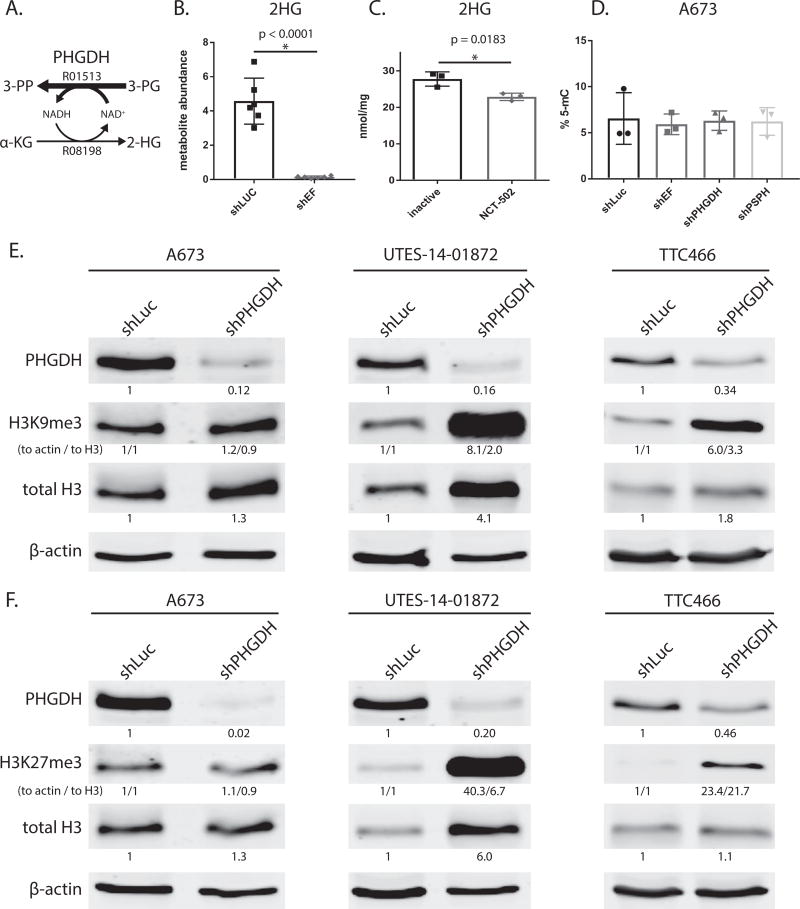
Figure 6. Modulation PHGDH causes decreased 2-hydroxyglutarate, and altered expression and methylation of histones.
A. Diagramatic representation of PHGDH enzyme function. PHGDH primarily catalyzes converion of 3-phospho-D-glycerate (3-PG) to 3-phosphoonoxypyruvate (3-PP), but also produces a minor product via conversion α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) to 2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG). KEGG reaction numbers are indicated. B & C. 2-hydroxyglutarate abundance as measured by GC-MS is lower in shEF vs. shLUC A673 cells. Inhibition of PHGDH by NCT-502 also decreases levels of 2-HG in A673 cells. D. LINE-1 methylation, a surrogate of bulk DNA methylation, is not different in shEF, shPHGDH or shPSPH vs. shLUC cells. E & F. In UTES-14-01872 and TTC466 cells, knockdown of PHGDH results in increased levels of histone H3 and increased methylation of H3 histones at lysine 9 and 27. This was not seen in A673 cells. A673 and UTES-14-01872 cell lines express EWS/FLI; TTC466 cells express the EWS/ERG fusion protein. For H3K9me3 and H3K27me3, both normalization to actin and normalization to total H3 are shown (indicated as “to actin / to total H3”).