Figure 1.
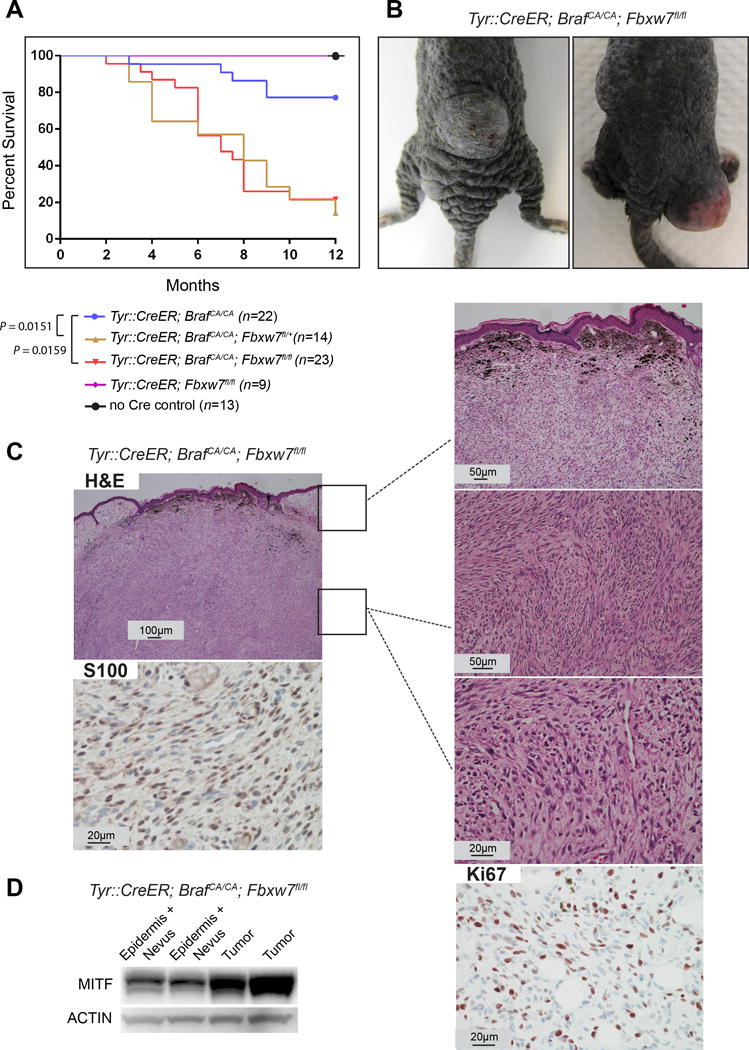
FBXW7 inactivation together with BrafV600E mutation cooperates in vivo to drive melanoma formation. (A) Survival curves of the mouse cohorts. Animals with tumor size greater than 1 cm3 or at 12 months after birth were euthanized. Log rank test was used for statistical analysis. (B) Representative examples of melanomas in the Tyr::CreERT2; BrafCA/CA; Fbxw7flox/flox mice are indicated. (C) Histology sections of the melanomas stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and immunohistochemistry for S100 and Ki67 are shown in the micrographs. (D) Tumors from Tyr::CreERT2; BrafCA/CA; Fbxw7flox/flox mice (without the overlying nevus cells and epidermis) were lysed and analyzed for MITF by western blotting. Actin was used as loading control.
