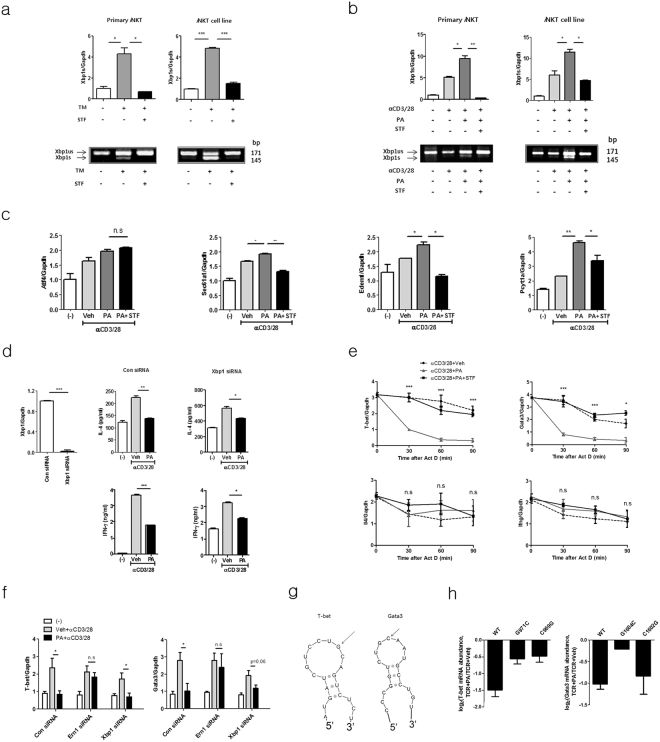
Figure 4.
Palmitic acid promotes the degradation of t-bet and gata-3 mRNA in iNKT cells via regulated IRE1α-dependent decay (RIDD), thereby suppressing IL-4 and IFN- γ production. (a and b) iNKT cells or α-GalCer/CD1d tetramer + TCRβ + iNKT cells sorted from C57BL/6 mouse liver mononuclear cells were treated with (a) tunicamycin (TM) and/or STF083010 or (b) palmitic acid and/or STF083010 in the presence of anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 mAbs. Reverse-transcription PCR and real-time PCR were performed to estimate un-spliced (us) or spliced (s) xbp-1. (c) The expression levels of Sec 61a1, Edem1, Pcyt1a and Atf4 were also measured in iNKT cells using real-time PCR. (d) To knock-down xbp-1, iNKT cells were transfected with control or xbp-1 siRNA and then treated with palmitic acid or vehicle in the presence of anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 mAbs for 24 h. The levels of IL-4 and IFN- γ were estimated in culture supernatants using ELISA. (e) The transcription levels of t-bet, gata-3, Il4, and Ifng were estimated in iNKT cells treated with vehicle, palmitic acid, or palmitic acid and STF083010 in the presence of actinomycin D at the indicated time points. (f) The transcription levels of t-betand gata-3 were measured in Ern1- or xbp-1-knockdown or control iNKT cells upon treatment with vehicle, palmitic acid, or palmitic acid and STF083010. (g) mRNA structural modeling for t-bet and gata-3. (h) DN32.D3 cells were transfected with mutant t-bet (G971C or C969G), mutant gata-3 (G1604C or C1602G), or wild type t-bet and gata-3 and then treated with palmitic acid or vehicle in the presence of anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 mAbs. mRNA measurement reflects the amount of relative degradation of t-bet or gata-3 transcript. n.s. not significant, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.005.