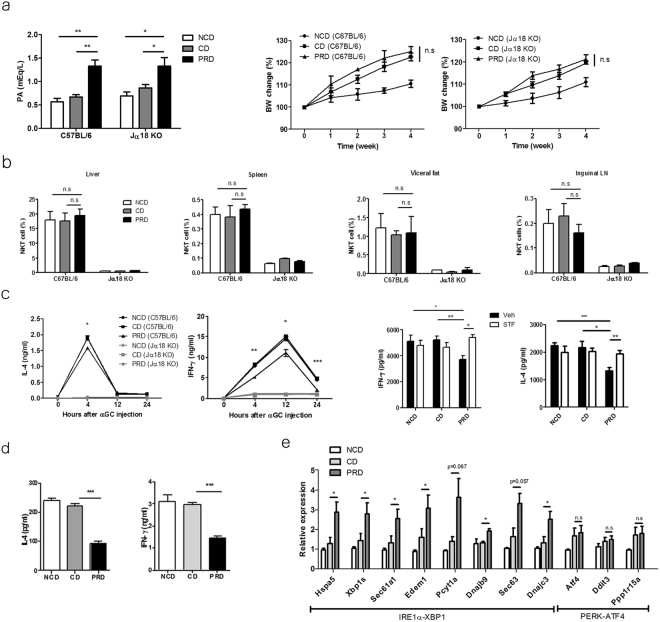
Figure 5.
Dietary palmitic acid inhibits IL-4 and IFN- γ production by iNKT cells via ER stress in the presence of TCR stimulation in vivo. (a) Serum levels of palmitic acid were estimated in C57BL/6 mice fed a normal chow diet (NCD), palmitic acid-rich diet (PRD), or a control diet (CD) for 4 weeks. The CD contained similar amount of calories as those of the PRD, but minimal palmitic acid. The serum concentration of palmitic acid and body weight of C57BL/6 and Jα18 Knockout (KO) mice were measured. (b) The percentages of iNKT cells in the visceral fat, liver, spleen, and inguinal lymph nodes were analyzed. The levels of IL-4 and IFN-γ in (c) the serum of C57BL/6 or Jα18 KO mice fed the NCD, CD, or PRD in the presence of (right panel) or absence (left panel) intraperitoneal STF083010 (20 mg/kg) injection every week for 4 weeks after α-GalCer injection and in (d) the supernatant of hepatic mononuclear cells from these mice in the presence of α-GalCer. (e) The expression levels of Hspa5, spliced xbp-1, Sec 61a1, Edem1, Pcyt1a, Dnajb9, Sec 63, Dnajc3, Atf4, Ddit3, and Ppp1r15a in hepatic iNKT cells obtained from C57BL/6 mice fed the NCD, CD, or PRD for 1 week using real time PCR. n = 12 per group in a; n = 6 per group in b, d and e; n = 9 per group in c. Data were pooled from three independent experiments and analyzed. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.005.