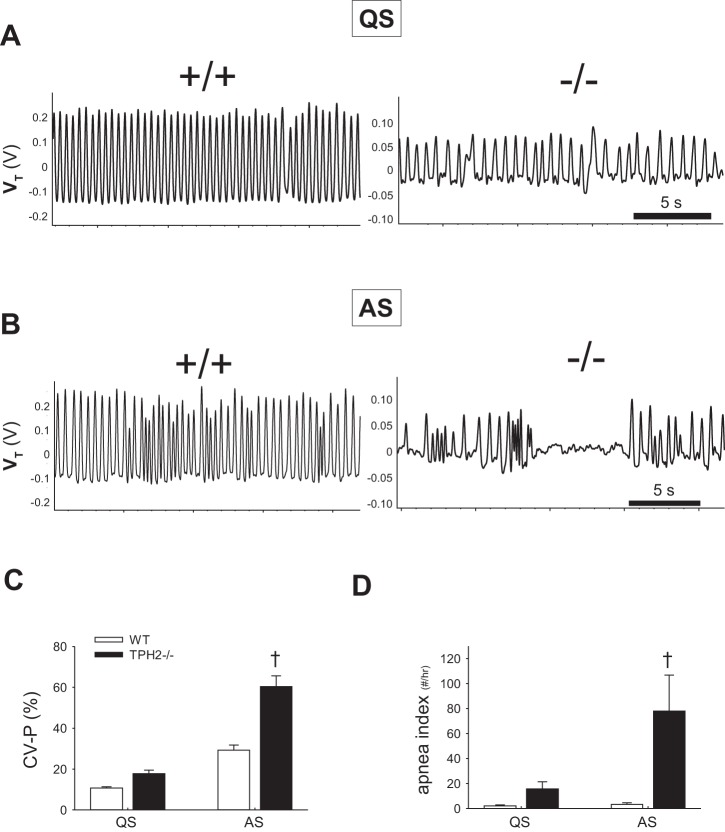
Fig. 3.
TPH2−/− pups are prone to severe apnea in active sleep. A: respiratory pattern of a TPH2+/+ (left) and a TPH2−/− (right) pup in quiet sleep (QS). B: respiratory pattern of a +/+ and a −/− pup in active sleep (AS). C and D: coefficient of variation of the respiratory period (CV-P%, C) and apnea index (no. of apneas/h, D) of TPH2+/+ (WT, n = 10) and TPH2−/− (n = 8) pups in quiet sleep (QS) and active sleep (AS). †CV-P% and apnea index of TPH2−/− higher than TPH2+/+ in AS only (effect of genotype within AS: P < 0.001).