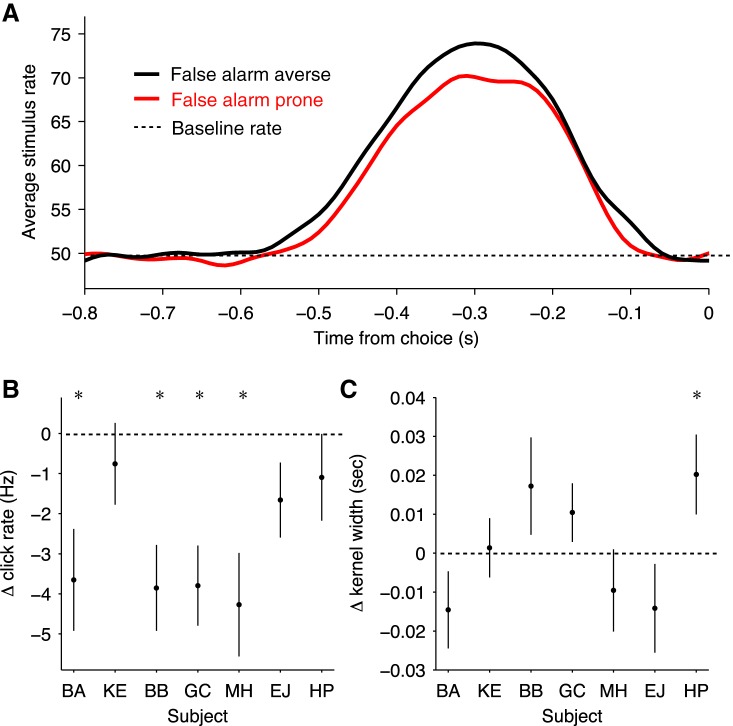
Fig. 4.
Psychophysical reverse correlation of temporal weighting of incoming information on the decision. A: average stimulus preceding false alarm responses for false alarm averse condition in black and miss averse condition in red. Stimulus rate was calculated by smoothing with a Gaussian filter having a width of 0.025 s. B: change in click rate preceding a false alarm response for each individual subject. Click rate was calculated in the window from 0.5 to 0.15 s before the choice response. Negative values indicate lower click rate in false alarm prone condition compared with the false alarm averse condition, and vice versa for positive values (subject BA: t = −2.89, P < 0.01, n = 347; subject KE: t = −0.74, P = 0.46, n = 403; subject BB: t = −3.60, P < 0.001, n = 360; subject GC: t = −3.80, P < 0.001, n = 502; subject MH: t = −3.31, P < 0.001, n = 390; subject EJ: t = −1.77, P = 0.08, n = 505; and subject HP: t = −1.01, P = 0.31, n = 481, where n refers to total number of false alarm trials). C: width of “kernel” derived from reverse correlation for each individual subject. The width is the portion of the reverse correlation kernel that exceeds the background rate and thus quantifies the temporal weighting of the sensory information preceding a response. Positive values indicate a wider kernel in false alarm prone condition compared with the false alarm averse condition, and vice versa for negative values (subject BA: t = −1.47, P = 0.14, n = 347; subject KE: t = 0.18, P = 0.86, n = 403; subject BB: t = 1.38, P = 0.17, n = 360; subject GC: t = 1.39, P = 0.17, n = 502; subject MH: t = −0.90, P = 0.37, n = 390; subject EJ: t = −1.25, P = 0.21, n = 505; and subject HP: t = 1.97, P < 0.05, n = 481, where n refers to total number of false alarm trials). Error bars indicate SE. *P < 0.05. Subjects BA, HP, and EJ were categorized as false alarm averse in the baseline sessions and false alarm prone in the instructed sessions. Subjects KE, BB, GC, and MH were categorized as false alarm prone in the baseline sessions and false alarm averse in the instructed sessions.