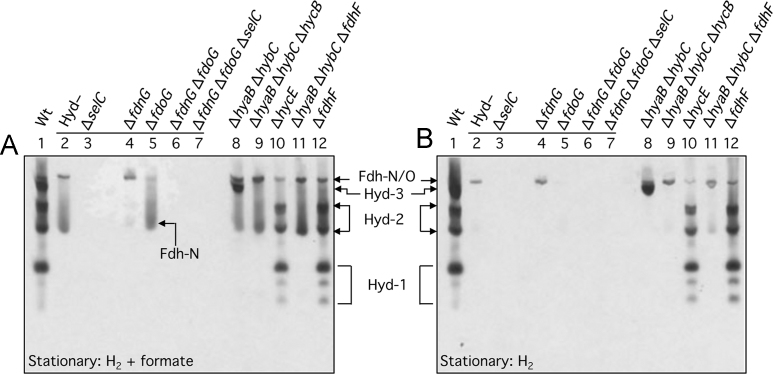
Fig. 3.
The Fdh-H enzyme lacks in-gel formate: BV-TTC oxidoreductase activity. Crude extracts (30 µg of protein) derived from the same E. coli strains shown in Fig. 1 were stained for Fdh and Hyd enzyme activities (A) or only Hyd activity (A) using the BV-TTC staining procedure (see Materials and methods). Cells were harvested when the cultures reached the stationary phase of growth. The strains included: Lane 1, MC4100 (wild type); lane 2, FTD147 (ΔhyaB, ΔhybC, ΔhycE); lane 3, SH1 (ΔhyaB, ΔhybC, ΔhycE, ΔselC); lane 4, SH173 (ΔhyaB, ΔhybC, ΔhycE, ΔfdnG); lane 5, SH174, (ΔhyaB, ΔhybC, ΔhycE, ΔfdoG); lane 6, SH175 (ΔhyaB, ΔhybC, ΔhycE, ΔfdnG, ΔfdoG); lane 7, SH200 (ΔhyaB, ΔhybC, ΔhycE, ΔfdnG, ΔfdoG, ΔselC); lane 8, CP734 (ΔhyaB, ΔhybC); lane 9, CP1002 (ΔhyaB, ΔhybC, ΔhycB); lane 10, HD705 (ΔhycE); lane 11, CP1010 (ΔhyaB, ΔhybC, ΔfdhF); lane 12, CP585 (ΔfdhF). The activity band(s) due to the respective enzyme complexes are indicated beside the panels. The migration position of a fast-migrating Fdh-N-dependent enzyme complex observed after activity staining in the presence of formate (A) is indicated within the figure.