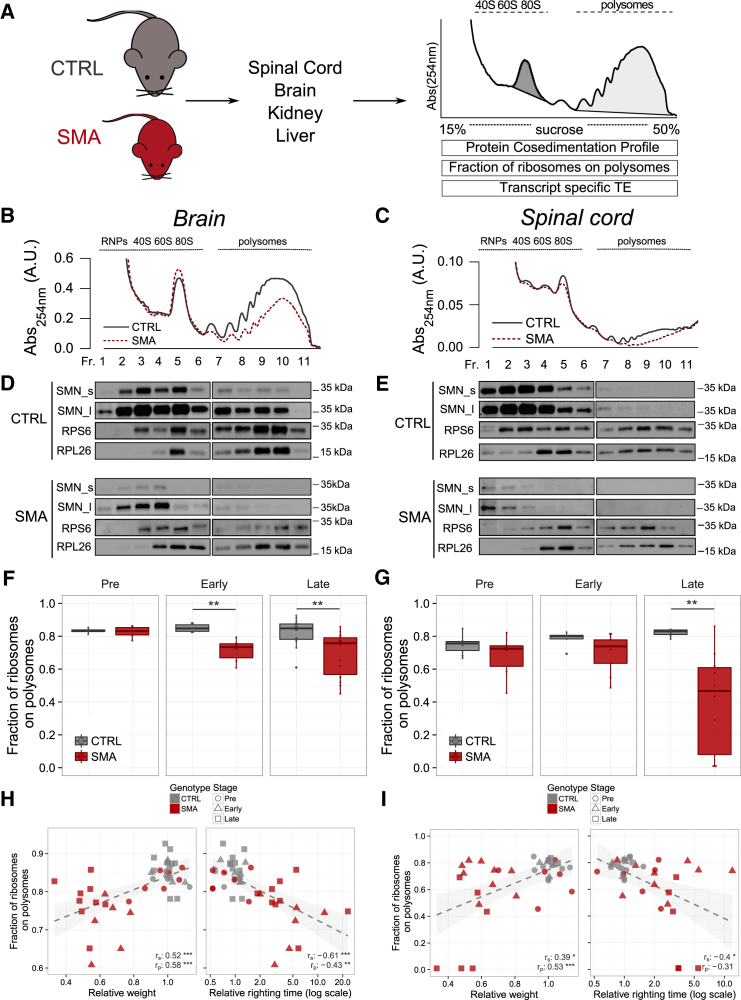
Figure 1.
Translation Is Impaired in Symptomatic SMA Nervous Tissues
(A) Experimental design and analyses using polysomal profiles from control (CTRL) and SMA mouse tissues.
(B and C) Sucrose gradient absorbance profiles from CTRL and SMA brains and spinal cords (late symptomatic).
(D and E) Co-sedimentation profiles of SMN and ribosome markers RPS6 and RPL26 under the corresponding sucrose gradient. The signal of SMN along the profile is shown for short (SMN_s) and long (SMN_l) exposure times of acquisition.
(F and G) Comparison between the fraction of ribosomes in polysomes (FRP) in CTRL and SMA mouse brains (F) and spinal cords (G) at three stages of disease (brain: pre-symptomatic, CTLR n = 4, SMA n = 7; early symptomatic: CTLR n = 6, SMA n = 6; late symptomatic: CTRL n = 16, SMA n = 14; spinal cord: pre-symptomatic: CTRL n = 7, SMA n = 6; early symptomatic: CTLR n = 5, SMA n = 9; late symptomatic: CTLR n = 7, SMA n = 10, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, two-tailed t test).
(H and I) Relationship between body weight (left) or righting time (right) and the corresponding FRP, obtained from CTRL and SMA mouse brains (H) and spinal cords (I). Each point corresponds to one mouse. Spearman and Pearson correlations between are indicated (∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, correlation test).