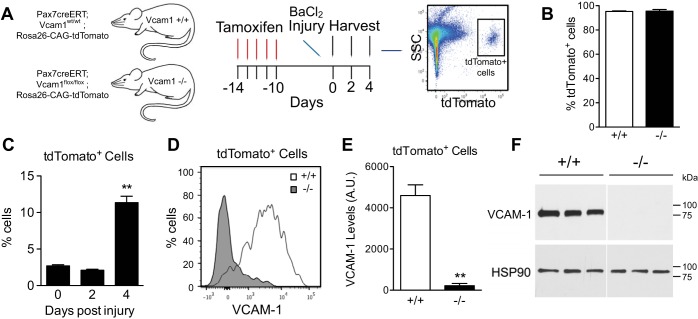
Fig. 1.
Efficient deletion of Vcam1 in satellite cells. A: schematic of Vcam1 deletion and tdTomato activation by tamoxifen treatment and analysis of tdTomato-positive (tdTomato+) cells by flow cytometry. SSC, side scatter. B: satellite cells isolated from tamoxifen-treated mice were >95% tdTomato+. Satellite cells were isolated by magnetic activated cell sorting (MACS) after negative selection for CD31, CD45, and Sca-1. C: the percentage of tdTomato+ cells increased during regeneration in gastrocnemius muscles. D: representative flow cytometry plot of VCAM-1 on tdTomato+ cells 2 days postinjury. E: quantification of average VCAM-1 surface level intensity on tdTomato+ cells. AU, artificial units. F: satellite cells were isolated by MACS, cultured for 7 days, and analyzed by immunoblotting for total cellular levels of VCAM-1. Immunoblot depicts that total VCAM-1 was efficiently eliminated in Vcam1−/− satellite cells. Heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) was utilized as a loading control. **P < 0.01; n = 3.