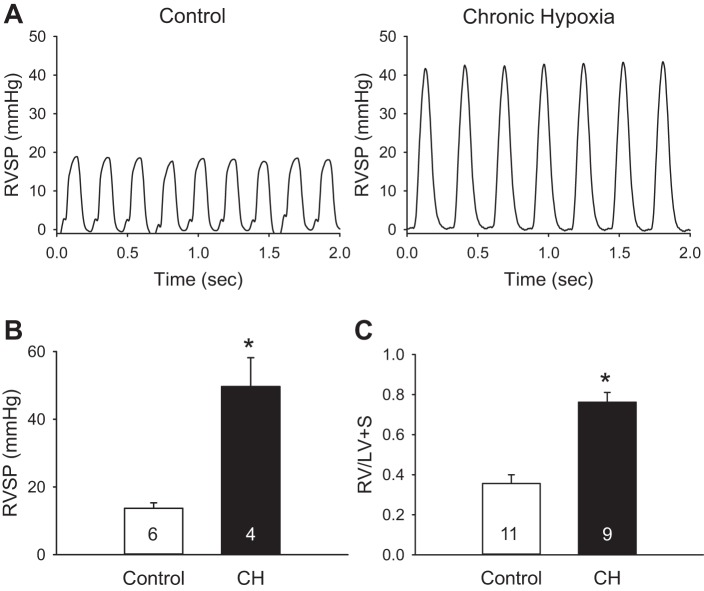
Fig. 1.
Chronic hypoxia (CH) increases peak right ventricular (RV) systolic pressure (RVSP) and induces RV hypertrophy in neonatal rats. A and B: sample pressure traces (A) and summary data (B) for peak RVSP in control and CH neonates. C: ratio of RV mass to left ventricular (LV) plus septal (LV + S) mass for each group. Values are means ± SE; n = 4–11/group (indicated in bars). *P < 0.05 vs. control, analyzed by unpaired t-test.