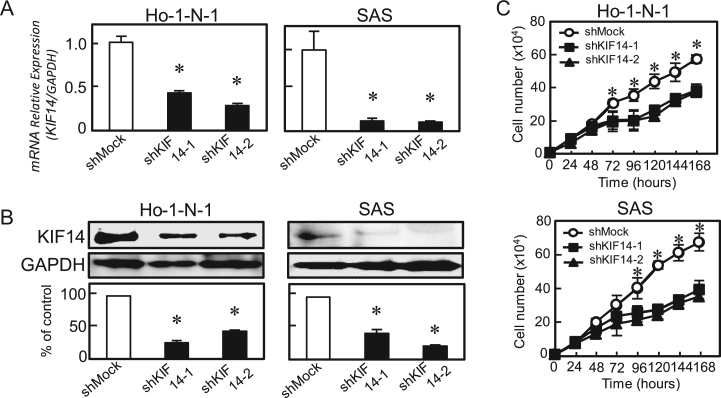
Fig. 3.
Establishment of KIF14 knockdown cells and cellular proliferation of KIF14 knockdown cells. (A) qRT-PCR shows that KIF14 mRNA expression in the shKIF14 cells (Ho-1-N-1-and SAS-derived transfectants; 2 clones each) is significantly (P<0.05, Mann–Whitney U-test) lower than in the shMock cells. (B) Immunoblotting analysis shows that the KIF14 protein levels in shKIF14 cells (Ho-N-1- and SAS-derived transfectants; 2 clones each) also have decreased markedly compared with that in the shMock cells. (C) To determine the effect of shKIF14 on cellular proliferation, shKIF14 and shMock cells were seeded in six-well plates at a density of 1×104 viable cells/well. Both transfectants were counted on seven consecutive days. The cellular growth of shKIF14 cells (Ho-1-N-1- and SAS-derived transfectants; 2 clones each) are significantly (P<0.05, Mann–Whitney U test) inhibited compared with the shMock cells after 72 (Ho-1-N-1) and 96 (SAS) hours. The results are expressed as the means±SEM of values from three assays.