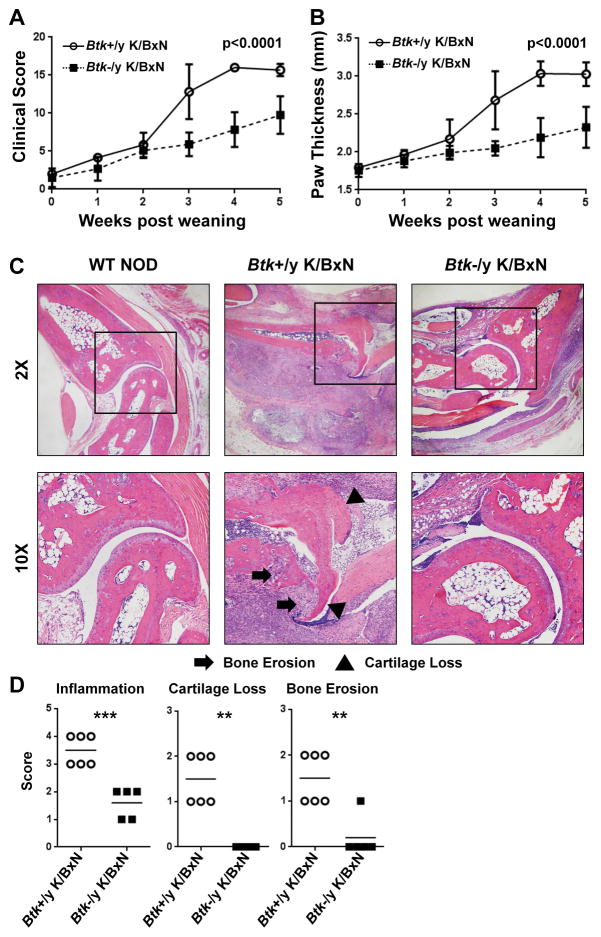
Figure 1. Btk deficiency is protective against the development of autoimmune arthritis in K/BxN mice.
A) and B) Btk-sufficient (circles, n=6) and Btk-deficient (squares, n=12) K/BxN mice were scored for arthritis for 5 weeks post weaning. Clinical scores (A) were assigned on a scale of 0–4 for each limb and pooled for a total possible score of 16. In addition, paw thickness (mm) was measured by caliper (B). Mean values are shown ± standard deviation. C) Representative H&E staining from right hind paws of WT NOD (left), Btk-sufficient K/BxN (middle), and Btk-deficient K/BxN (right). 2X magnification (top), 10X magnification (bottom). Arrows indicate areas of bone erosion, triangles indicate cartilage loss. D) Scoring of Btk-sufficient (circles, n=6) or –deficient (squares, n=5) for inflammation (top), cartilage loss (middle), and bone erosion (bottom). Inflammation was scored on a scale of 0 to 4, while cartilage loss and bone erosion were scored as 0 to 2. P values were calculated by a 2-way AVOVA with Sidak correction (A, B) **p≤0.01, ***p≤0.001, by unpaired T test with Welch’s correction (D).