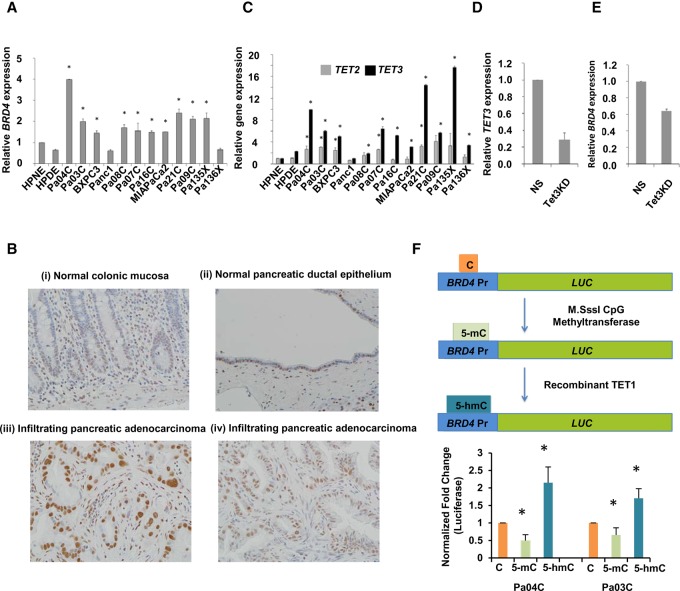
Figure 6.
BRD4 and TET3 are overexpressed in pancreatic cancer, and BRD4 expression correlates with acquisition of 5-hmC at the promoter. (A) qRT-PCR for BRD4 expression shows significant increase in pancreatic cancer cell lines when compared to controls (t-test, P-value <0.05 for all pancreatic cancer samples when compared to HPNE control). (B) IHC for BRD4 shows specific staining in pancreatic cancer cells: normal colonic mucosa with weak staining restricted to basal crypt epithelium (i); normal pancreatic ductal epithelium with patchy nuclear BRD4 labeling (ii); infiltrating pancreatic adenocarcinoma with diffuse strong nuclear BRD4 labeling (iii); and independent example of Infiltrating pancreatic adenocarcinoma with diffuse strong nuclear BRD4 labeling (iv). (C) qRT-PCR for TET2 and TET3 shows higher fold change increase for TET3 in pancreatic cancer cells when compared to controls (t-test, P-value <0.05 for pancreatic cancer samples when compared to HPNE control). (D) qRT-PCR for TET3 shows significant reduction with Pa04C cells with TET3 shRNA when compared to nonsilencing (NS) controls (t-test, P-value <0.05, N = 2). (E) qRT-PCR for BRD4 shows significant reduction with Pa04C cells with TET3 shRNA when compared to nonsilencing (NS) controls (t-test, P-value <0.05, N = 2). (F) Luciferase promoter for BRD4 was methylated and hydroxymethylated in vitro and shows significantly increased expression after 5-hmC acquisition (t-test, P-value <0.05, N = 4).