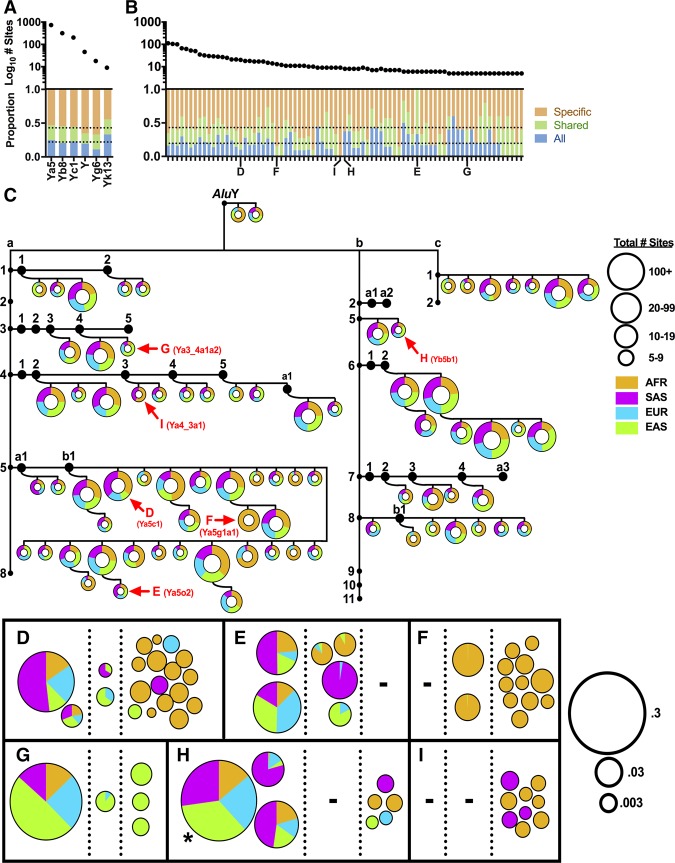
Figure 2.
Complex patterns of Alu subfamily expansion in diverse human populations. Six known Alu subfamilies (A) and 79 novel Alu subfamilies (B) that were identified using interior sequence changes were analyzed for sharing among the 1000 Genomes Project nonadmixed continental populations. Plotted are: (top) log10 total sites in each subfamily; (bottom) proportion of sites shared among all continental populations (blue); proportion of sites shared by two or three continental populations (green); proportion of sites that are specific to one continental population (brown). The average proportion for each category is indicated by a horizontal dotted line. (C) Tree of 79 novel AluY subfamilies. We required at least five independent copies with a novel set of interior mutations (excluding CpG sites) to establish new subfamilies. This threshold is fairly conservative and eliminates errors introduced by Illumina sequencing. After CAlu classification (Supplemental Fig. S9), novel Alu subfamilies were placed on a tree of known AluY families (a, b, and c shown) and subfamilies (small black circles). Each pie chart represents the sum of allele counts for all constituent sites of a particular novel subfamily with the total number of identical loci represented by the diameter of the pie (see Supplemental Fig. S10 for figure key). (AFR) African; (SAS) South Asian; (EUR) European; (EAS) East Asian. (D–I) Families with unique population sharing are shown, with each pie representing the proportion of total alleles from each of the four major continental populations of the 1000 Genomes Project. Each site is placed into one of three categories based on population sharing: present in all four continental populations (left); in two or three continental populations (middle); or in one continental population (right). Pies are sized based on the log10 allele frequency of each site. (*) Actual AF is 0.52446. Alu subfamilies were named as outlined in Batzer et al. 1996 (Supplemental Table S8).