Fig. 6.
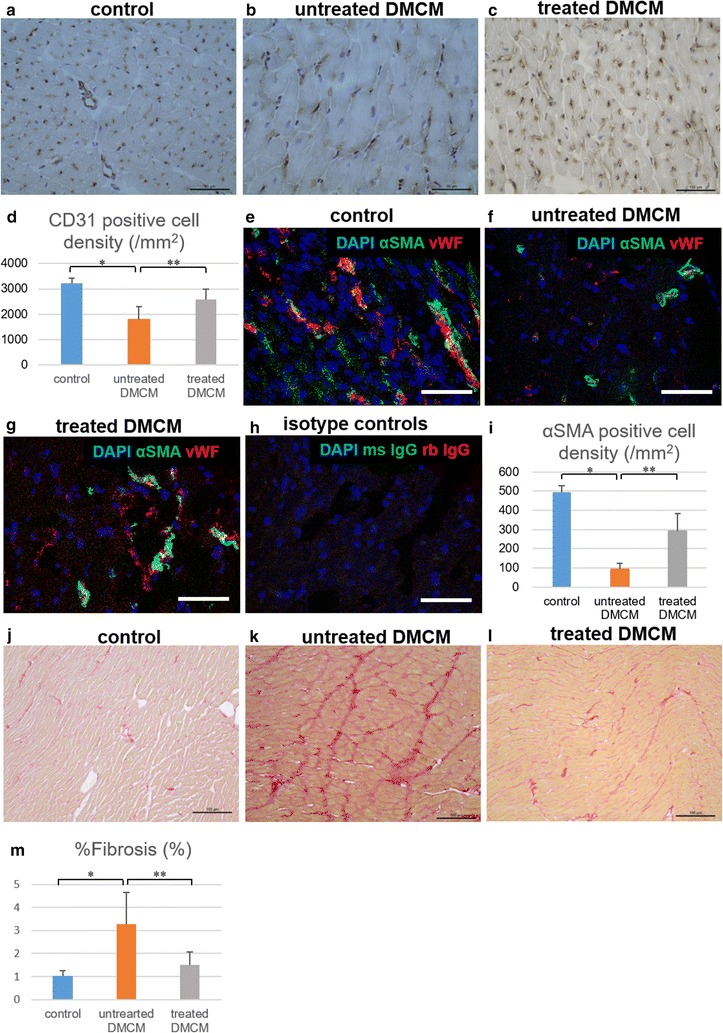
Histological evaluation reveals increased microvascular density and decreased interstitial fibrosis following SMC-EPC bi-level cell sheet implantation with successful EPC integration. a–i Microvascular density at 4-week study end-point in the control group (a, e), untreated group (b, f), and cell sheet-treated group (c, g) assessed semi-quantitatively by immunohistochemistry for CD31 and αSMA showed significantly enhanced microvascular density in the cell sheet-treated group (d, i). Image of isotype controls was also provided (h). j–m Semi-quantitative evaluation of interstitial fibrosis in the control group (j), untreated group (k), and cell sheet-treated group (l) demonstrates significantly less interstitial fibrosis in animals treated with cell sheet implantation as compared to untreated animals (m). Image scale bars, 100 µm in a–c, j–l, 50 µm in e–h; *P < 0.001, **P < 0.05. αSMA alpha smooth muscle actin, CD31 cluster of differentiation-31, DAPI 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, DMCM diabetic cardiomyopathy, ms IgG mouse immunoglobulin G, rb IgG rabbit immunoglobulin G, vWF von Willebrand factor
