Fig. 1.
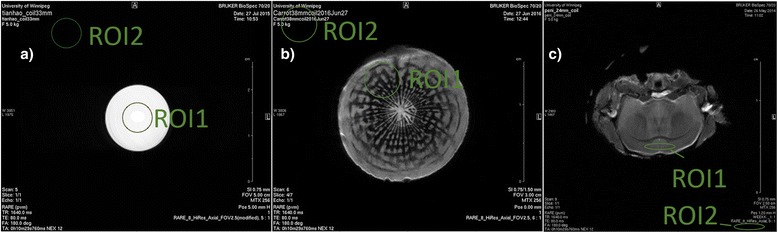
Sample axial (i.e. cross-sectional) images from each of the samples. A typical image of a 14 mm diameter sample tube, filled with a water-based 0.1 M CuSO4 solution, is shown in (a). This particular image was collected with a 33 mm diameter 50 mm long birdcage volume RF coil. Two identical regions, one within the sample tube (labeled ROI1) and one outside the sample tube (labeled ROI2), were drawn on the figure using the standard issue software, Bruker Paravision 5.0, of the imager to select the regions for analysis. The first ROI is meant to represent the signal within the sample and the second region represents the background signal from noise in the image. The software returned the mean and standard deviation of the signal in each of the regions. Example images for a 17.1 mm diameter carrot and a 9.3 mm wide mouse brain are shown in Figure (b and c) respectively with similar ROIs. Note that the mouse brain image is an axial image presented as though the mouse was lying on its back
