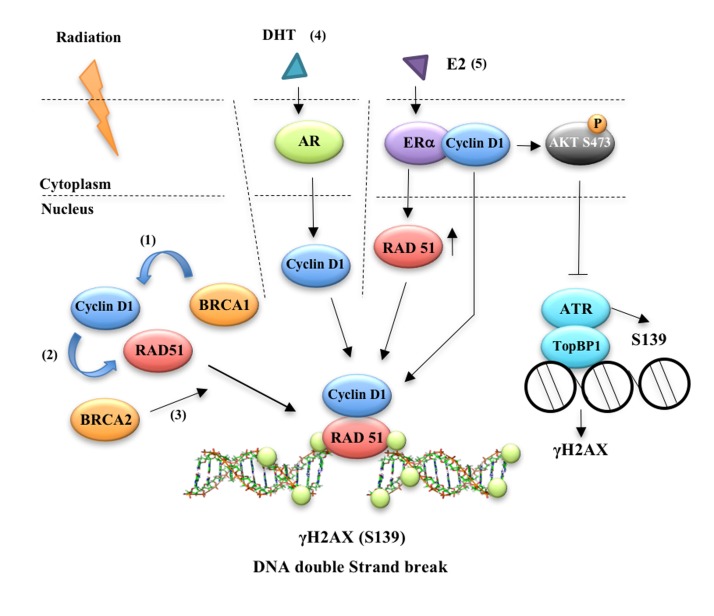
Figure 1. Cyclin D1 participates in estrogen and androgen mediated DNA damage repair responses.
Cyclin D1 binds (1) BRCA1 [6], (2) RAD51 ([7, 8]) and (3) BRCA2 [8]. Cyclin D1 was required for the (4) androgen-mediated DNA damage response both in vitro and in vivo suggesting hormone-mediated recruitment of cyclin D1 to sites of DDR may facilitate the resistance of prostate cancer cells to radiotherapy [10]. Silencing cyclin D1 leads to an impairment of DNA DSBs repair and a physical interaction was identified between cyclin D1 and activated ATM, DNA-PKcs and RAD51. Taken together these data suggest a key role for cyclin D1 in regulating the androgen-dependent DDR response [11]. (5) Using estrogen dendrimers that are excluded from the nucleus, Li et al showed that E2-mediated cyclin D1 dependent DDR occurred via a novel extra-nuclear function. Their findings revealed that ERα-cyclin D1 binding at the cytoplasmic membrane augmented AKT phosphorylation (Ser473) and γH2AX foci formation. In the nucleus, cyclin D1 enhanced homology-directed DNA repair. Cyclin D1 was recruited to γH2AX foci by E2 and induced Rad51 expression [9].