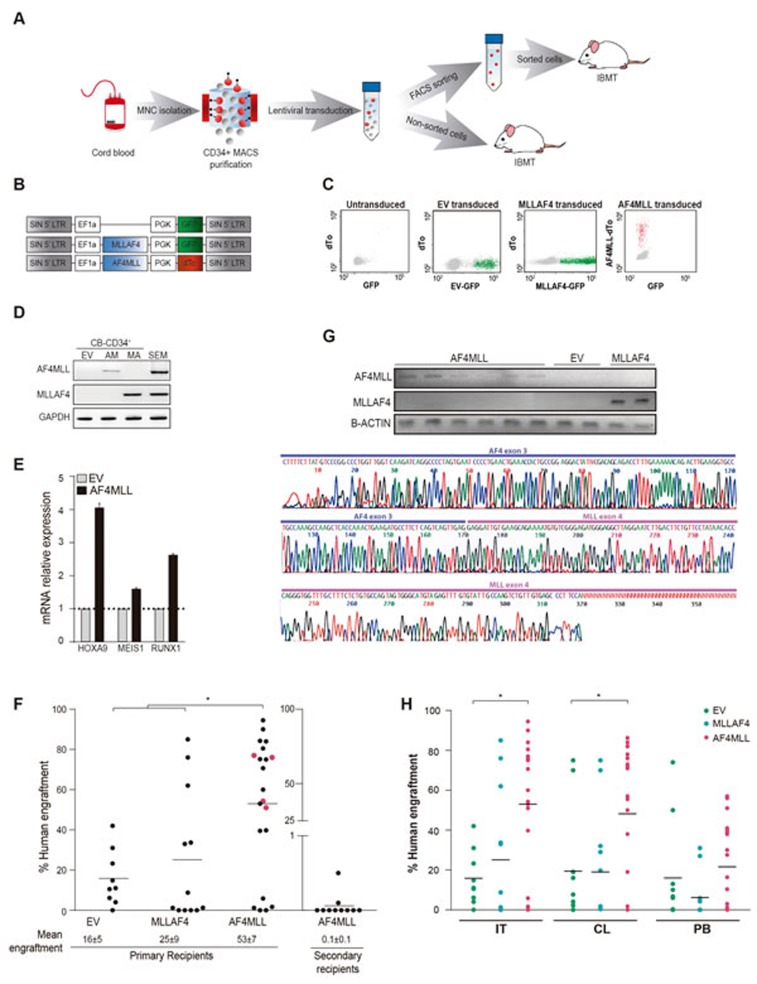
Figure 1. Expression of AF4-MLL enhances hematopoietic engraftment of CB-CD34+ HSPCs.
A. Outline of the experimental design. B. Schematic representation of the lentivectors used. AF4-MLL and MLL-AF4 vectors express dTomato and GFP, respectively, as reporter. C. Representative flow cytometry plots showing FACS purification of transduced cells: GFP+ cells (green) in MLL-AF4-transduced, dTo+ cells (red) in AF4-MLL-transduced CD34+ HSPCs. Mock-transduced cells (left panel) were used as a reference control. D. RT-PCR confirming ectopic expression of AF4-MLL and MLL-AF4 in transduced CB-CD34+ cells. E. RT-qPCR confirming upregulation of the AF4-MLL downstream effectors HOXA9, MEIS1 and RUNX1 in transduced cells. F. Levels of long-term (36 weeks) hematopoietic engraftment of CB-CD34+ expressing AF4-MLL or MLL-AF4 (n = 42 mice). Note the very limited hematopoietic engraftment of AF4-MLL-expressing CB-CD34+ upon serial (secondary) xenotransplantation (n = 12 mice from 4 independent experiments corresponding to primografts shown in pink). G. Upper panel: RT-PCR confirming stable ectopic expression of AF4-MLL and MLL-AF4 in xenografts recovered 36 weeks after transplantation. Lower panel: Sanger sequencing verifying the AF4-MLL PCR product. H. Hematopoietic engraftment in the injected tibia (IT), the contralateral (CL) tibia and the PB of EV, MLL-AF4 and AF4-MLL primografts 36 weeks after transplantation. MNC: Mononuclear cells; EV: Empty vector; IBMT: Intra-bone marrow transplantation.