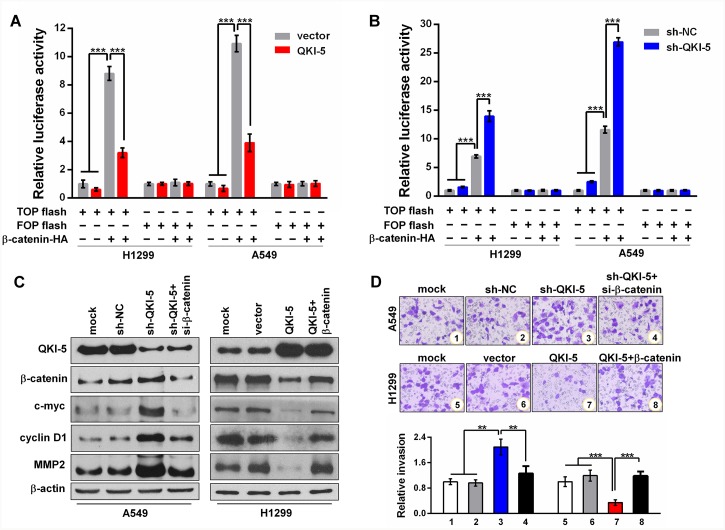
Figure 4. QKI-5 suppresses LC cell invasion by blocking β-catenin signaling pathway.
(A and B) Relative luciferase activities in subcell lines of control (H1299-vector, A549-vector) and QKI-5 expression (H1299-QKI-5, A549-QKI-5) (A), or in subcell lines of control (H1299-sh-NC, A549-sh-NC) and QKI-5 knockdown (H1299-sh-QKI-5, A549-sh- QKI-5) (B), co-transfected with TOP or FOP flash plus β-catenin-expressing plasmid (β-catenin-HA) as β-catenin/TCF/LEF pathway activator, and β-galactosidase-expressing plasmid as transfection efficiency control. TOP flash=the reporter plasmid containing three wild type binding sites of β-catenin-TCF/LEF complex in its luciferase promoter, FOP flash=the negative control plasmid containing the mutated binding sites of β-catenin-TCF/LEF complex. The data were normalized according to the ratio of firefly luciferase activity to the β-galactosidase value. (C) Protein levels of QKI-5, β-catenin, c-myc, cyclin D1 and MMP2 detected by Western blotting in the indicated cells. (D) Representative images (upper) and quantitative data (bottom) of invasion of the indicated A549 and H1299 cells assessed by transwell assay. All the experiments were performed at least in triplicate and the data in A, B and D are presented as the mean ± SD. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.