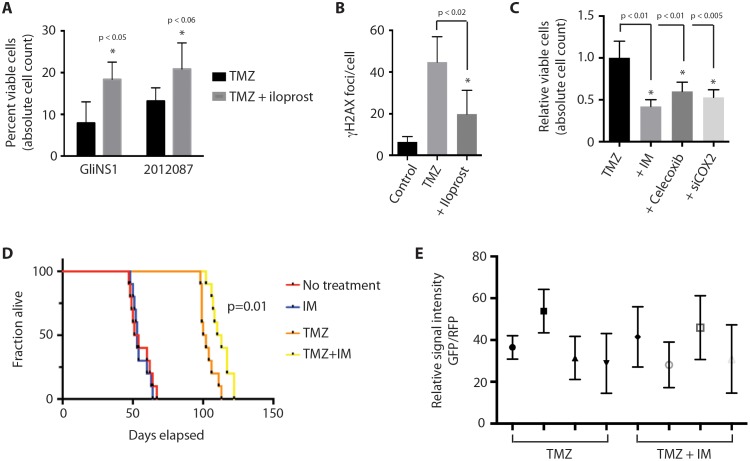
Figure 7. COX-2 inhibition enhances the cytotoxic effect of temozolomide in glioblastoma.
(A) Concurrent treatment of GSCs with iloprost (100 μM) protects GSCs (GliNS1, 2012087) from the cytotoxic effect of temozolomide (50 μM), as determined by absolute cell count. (B) γH2AX foci in GliNS1 GSCs treated with temozolomide (50 μM) with or without iloprost (100 μM). (C) Concurrent Cox inhibition with indomethacin (IM) or Cox-2 inhibition with celecoxib (50 μM) or siRNA against COX-2, potentiates the cytotoxic effect of temozolomide (50 μM) on GliNS1 GSCs. (D) Kaplan-Meier curve showing survival in a mouse glioblastoma orthotopic xeongraft. Treatment with the Cox inhibitor indomethacin had no direct effect on overall survival, but enhanced the survival benefit proffered by treatment with temozolomide. (E) No statistically significant difference (p=0.46) in the relative percentage of nuclear β-catenin-positive cells among surviving RFP-positive glioma cells in xenograft-harboring mice treated with temozolomide and indomethacin (n=4) compared to xenograft-harboring mice treated with temozolomide alone (n=4). Data are represented as mean ± SEM.