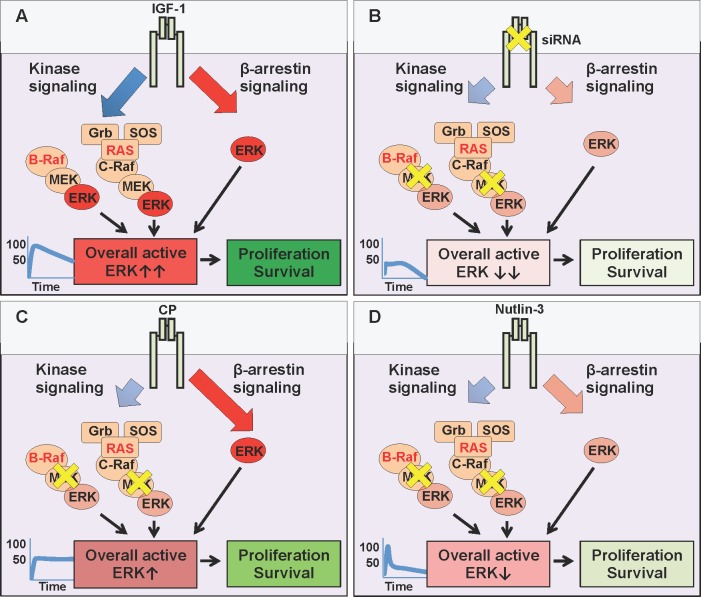
Figure 5. MEK and IGF-1R co-targeting.
(A) The natural (balanced) ligand, Insulin-like growth factor type 1 (IGF-1) binds to the IGF-1R and activates all downstream signaling pathways simultaneously: canonical kinase signaling (MAPK and PI3K/Akt (not shown)) and kinase-independent β-arrestin signalling (MAPK). In conditions with either BRAF or RAS mutations, the overall ERK activity is very high (graph, ↑↑) driving cellular survival and proliferation. (B) Targeting the IGF-1R with small interfering RNA (siRNA) prevents the translation of IGF-1R mRNA, thus reducing receptor levels at the cell surface (inhibition - yellow X), limiting all downstream pathways (kinase and β-arrestin). Small molecule U0126 further inhibits MEK, downstream of hyperactive RAS or BRAF. When combined, the resultant overall ERK activity is severely impaired (↓↓), decreasing cellular survival and proliferation. (C) Targeting the IGF-1R with specific antibody Figitumumab (CP-751871 (CP)) promotes receptor down-regulation, limiting its cell surface expression. However, this down-regulation triggers IGF-1R kinase-independent β-arrestin signaling (biased agonist). In co-targeting, this β-arrestin generated ERK activity competes with MEK inhibition (U0126), and resultant overall ERK activity remains high enough (↑),to sustain cellular survival and proliferation. (D) Targeting the IGF-1R with small molecule Nutlin-3 promotes receptor down-regulation, with transient β-arrestin signaling, insufficient to compensate for MEK inhibition. Reduced receptor expression combined with MEK inhibition, keeps overall ERK activity very low (↓) reducing cellular survival and proliferation.