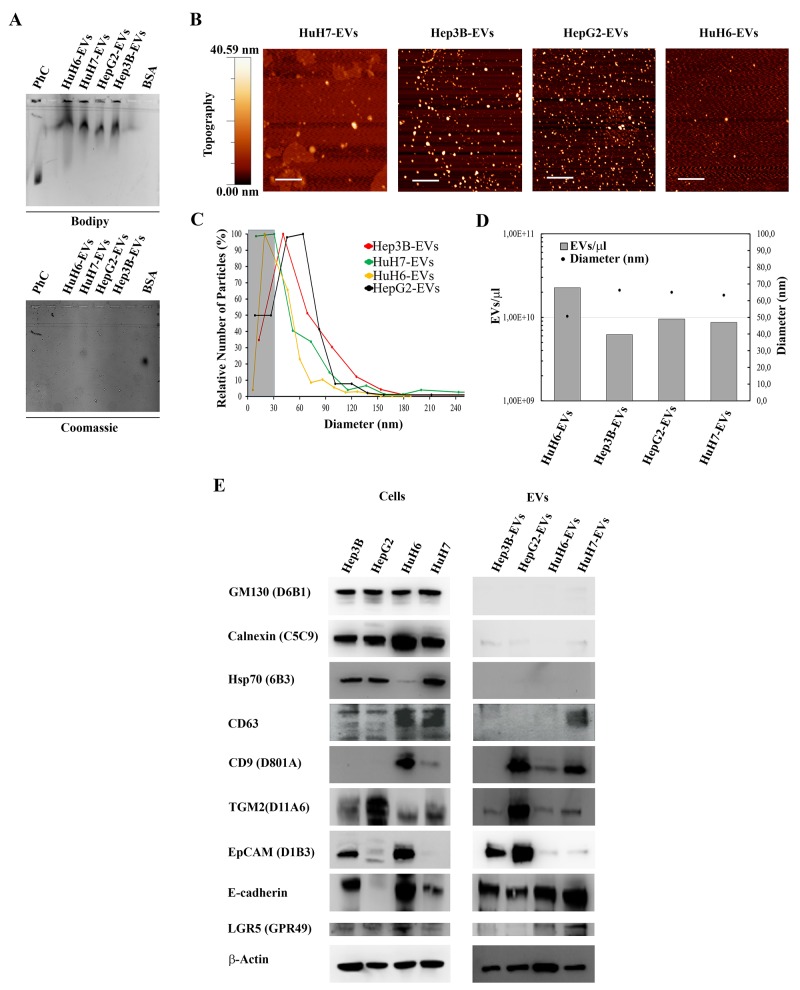
Figure 1. Characterization of human LCC derived extracellular vesicles (HuH7-EVs, Hep3B-EVs HepG2-EVs and HuH6-EVs).
(A) EV preparations electrophoretic mobility: 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (POPC) liposomes (270 nM) and vesicle samples were stained with green fluorescent dye (BODIPY FL C5-HPC) and run on a 0.6% agarose gel together with BSA solution (1μg/μL). Gel was also stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue dye to evidence samples protein content and possible exogenous contaminants. (B) AFM topography image of the four EV preparations. Scale bars are 1 μm. (C) Size distribution of EV samples. Around 150-250 objects with a diameter between 0 and 250 nm were analyzed for each preparation using the WSxM 5.0 software. The EV diameter (nm) of each EV population was plotted against the relative number of particles (%). Objects with a diameter lower than 30 nm were not included in the analysis (darken plot area). (D) For each sample, weighted mean diameter values (nm) have been plotted together with sample concentration values (EV/μL) obtained by nanoplasmonic colorimetric assay [45]. (E) Representative western blots showing the expression of: GM130, calnexin, Hsp70, CD63, CD9, TGM2, EpCAM, E-cadherin, LGR5 and β-actin in LCC and LCC-derived EVs. Experiments were performed with similar results.