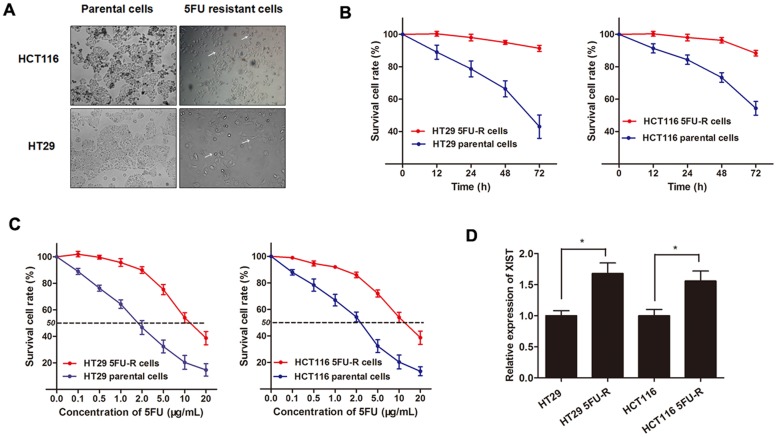
Figure 4. XIST is up-regulated in 5FU-resistant CRC cell lines.
(A) The CRC cell line HT29 and HCT116 that had acquired resistance to 5FU at the clinically relevant concentration of 2 μg/mL were built as described in Methods. The built 5FU-R cells induced specific morphologic changes consistent with epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), including loss of cell polarity causing a spindle-cell morphology, increased intercellular separation signifying loss of intercellular adhesion, and increased formation of pseudopodia (arrows). (B) Both HT29 5FU-R and HCT116 5FU-R cells showed elevated cell viability compared to HT29 and HCT116 parental cells when incubated with culture medium containing 2 μg/mL concentration of 5FU. (C) The concentration-effect curve indicated that the IC50 values of 5FU for HT29 5FU-R (11.5 μg/mL) and HCT116 5FU-R cells (10.95 μg/mL) were significant higher than that for HT29 (1.85 μg/mL) and HCT116 parental cells (2.33 μg/mL). (D) The expression of XIST in HT29 5FU-R and HCT116 5FU-R cells were significantly higher than that in HT29 and HCT116 parental cells, respectively. Error bars represent SD. *, P<0.05 by Mann-Whitney U test.