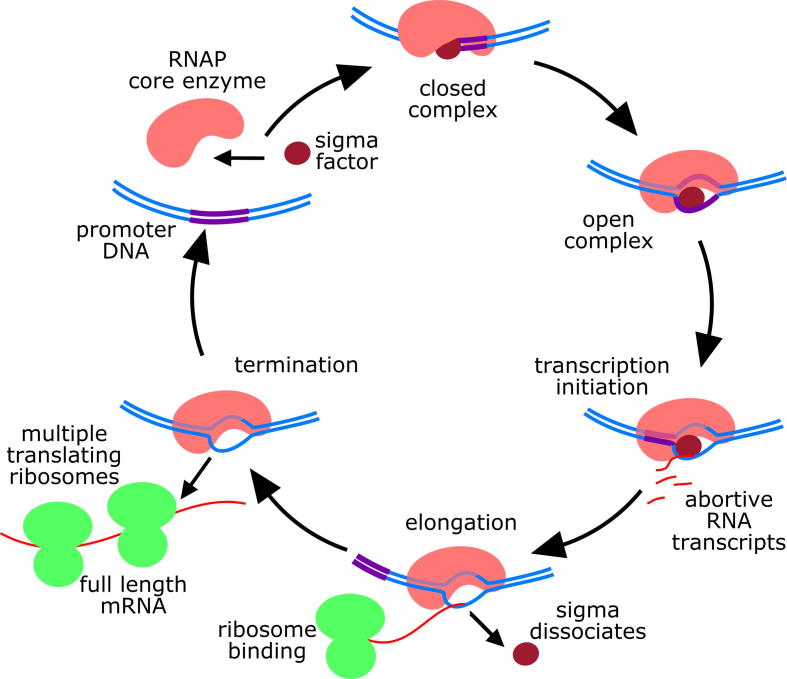
Fig. 1.
The transcription cycle. RNAP associates with a sigma factor before binding to a promoter site. After initial binding, the enzyme opens a bubble in the duplex DNA to form an ‘open complex’. From here, it can initiate transcription; however, on many promoters, the polymerase makes several attempts to start transcribing, generating short abortive RNAs [14]. Once past the ∼10th nucleotide, the RNAP breaks its interactions with promoter DNA and enters into processive synthesis of RNA as an ‘elongation complex’. At some point during elongation, the sigma factor usually dissociates from the core enzyme [6]. Finally, RNAP reaches the end of the gene, and the RNA transcript and the core enzyme dissociate from DNA.