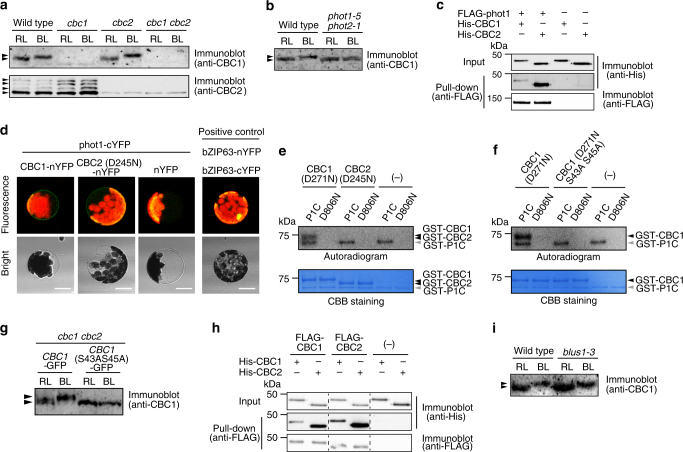
Fig. 4.
Phosphorylation of CBC1 by phototropin1 in a BL-dependent manner. a BL-dependent mobility shift of CBC1. GCPs were illuminated with light as described in Fig. 1a. Samples were obtained 1 min after the start of the BL pulse. Immunoblot analysis of CBC1 was performed after electrophoresis on Phos-tag SDS-PAGE that contained 10% acrylamide, 20 μM Phos-tag, and 40 μM MnCl2. For CBC2, 40 μM Phos-tag and 80 μM MnCl2 were included in the gel. b Phototropin-mediated phosphorylation of CBC1. CBC1 detection was done as described in a. c Pull-down assays of CBC1 and CBC2 by phot1. FLAG-phot1 and His-CBCs were synthesized in vitro transcription/translation. d BiFC assays of CBCs and phot1. CBCs-nYFP and phot1-cYFP were co-transfected to MCPs. White bars represent 20 μm. e Phosphorylation of kinase-dead CBC1 (D271N) and CBC2 (D245N) by P1C using [γ-32P] ATP. Phosphorylation assays were performed in 30 μl reaction mixtures that contained 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 10 mM MgCl2, 3.3 μM ATP, 20 μCi of [γ-32P] ATP, and purified proteins. The reactions proceeded for 2 h at 15 °C. GST-tagged P1C or kinase-dead P1C (D806N) were included at 2.5 μg, and CBC1 (D271N) and CBC2 (D245N) were added at 1.2 μg. These GST proteins were expressed in E. coli and purified with glutathione-Sepharose beads. f Phosphorylation of kinase-dead CBC1 (D271N) and CBC1 (D271N S43A S45A) by P1C. Measurement was done as same as e. g Mobility of CBC1-GFP and CBC1 (S43A S45A)-GFP expressed in guard cells was determined as a, except the acrylamide concentration was used at 6%. The cbc1 cbc2 double mutant was transformed with CBC-GFP or CBC1 (S43A S45A)-GFP and GCPs were prepared from these transgenic plants. h Pull-down assays of His-CBC1 and His-CBC2 by FLAG-tagged CBC1 and CBC2. Tagged proteins were synthesized by in vitro transcription/translation. i BL-dependent phosphorylation of CBC1 in the blus1-3 mutant. CBC1 detection was done as described in a