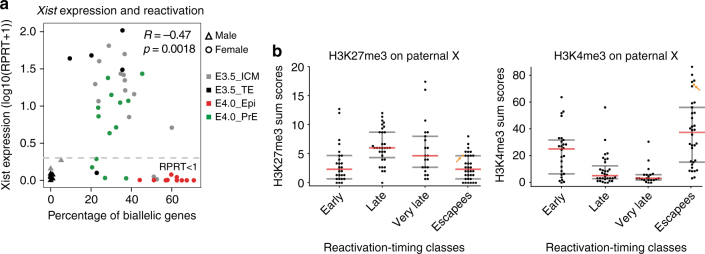
Fig. 5.
Link between Xist expression, epigenetic landscapes and Xp reactivation. a Anti-correlation is shown between the level of Xist expression and the number of biallelically/reactivated and informative X-linked genes in scRNAseq (Spearman correlation). Male E3.5 single cells have been added and used as control for Xist expression and X-linked gene parental expression. Genes with level of expression as (RPRT <1) are considered as non-expressed in our samples. b Enrichment of H3K27me3 and H3K4me3 on paternal X-chromosome obtained from Zheng et al.38 shows significant differences (by Wilcoxon test) between early and escapee reactivation-timing classes compared to late and very late. Low cell chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIPseq) have been performed with ICM cells of pre-implantation embryos (pooled between E3.5–E4.0) after immunosurgery of the ICM38. Activated genes show an excess of H3K4me3 and repressed ones an enrichment of H3K27me3. Xist is highlighted with an orange arrow. Early vs. late (p = 2.29 × 10−4 for H3K27me3 and p = 1.63 × 10−3 for H3K4me3) and very late (p = 2.51 × 10−2 for H3K27me3 and p = 3.95 × 10−4 for H3K4me3) and escapees vs. late (p = 1.95 × 10−6 for H3K27me3 and p = 2.09 × 10−7 for H3K4me3) and very late (p = 7.33 × 10−3 for H3K27me3 and p = 6.73 × 10−8 for H3K4me3) by Wilcoxon test