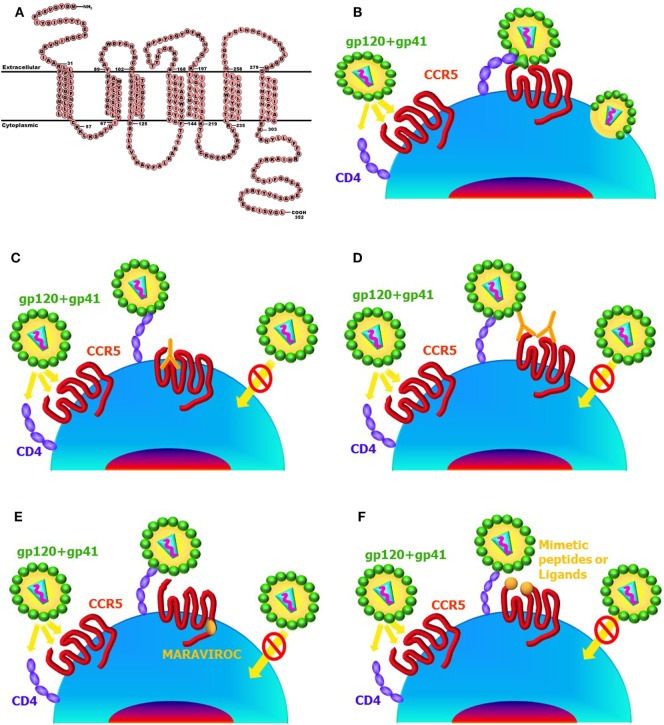
Figure 2.
Main anti-CCR5 strategies working at target cell surface. CCR5 protein sequence (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CCR5#/media/File:CCR5_Primary_Protein_Sequence.png) (A). HIV entry process (B). Natural antibodies (Abs) to CCR5 bind to the ECL1 domain, induce long-lasting internalization of the receptor, and block HIV infection (C). Abs to either N-terminus or ECL2 domains of CCR5 compete with HIV-binding site and interfere with HIV infection (D). CCR5 allosteric modulators, such as MARAVIROC, do not allow HIV entry (E). Ligands (such as RANTES or its modified analogous) bind to the ECL2 or mimetic peptides bind to the either N-terminus or ECL2 and interfere with HIV entry process (F).