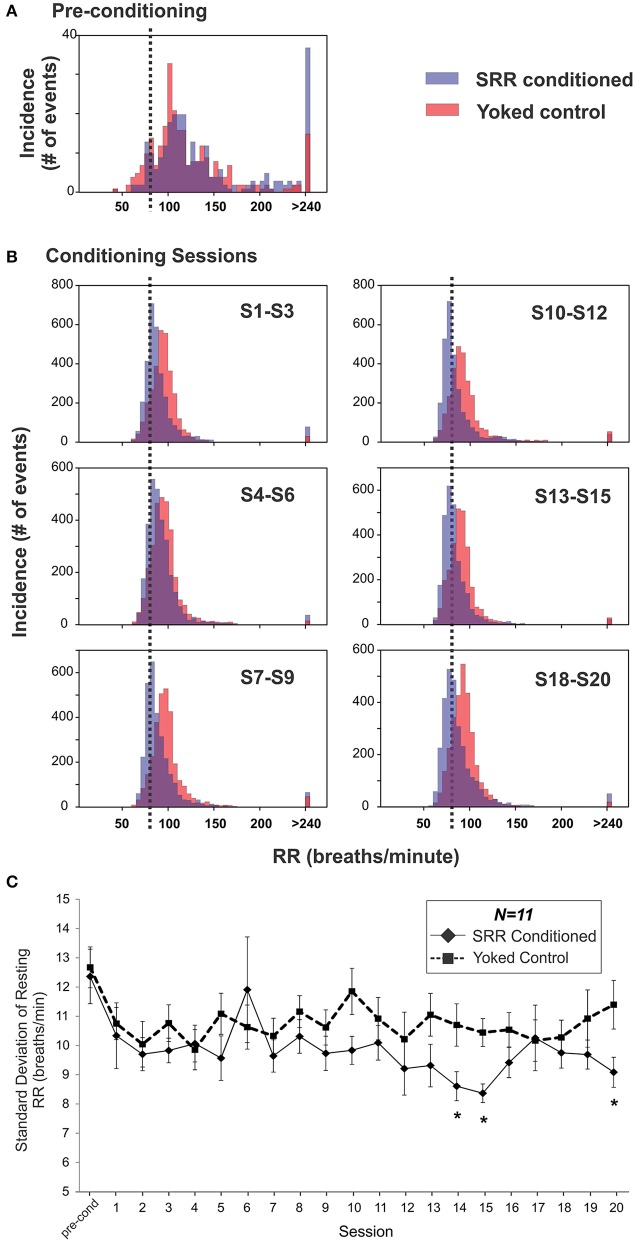
Figure 4.
Respiration became slower and more regular over 20 sessions in SRR conditioned rats. (A,B) SRR conditioning led to a leftward shift in RR values and a skewed distribution centered just below the target RR. Shown are frequency histograms depicting the number of occurrences of different instantaneous RRs (5 breaths/min bins) over one 2 h pre-conditioning period or three conglomerated 2 h conditioning sessions in a representative pair of SRR conditioned (blue) and yoked control (red) animals. (A) Distributions during pre-conditioning. (B) Frequency histograms show the gradual leftward shift in RRs. Decreased rates (on the x-axis) are easily visualized in the conditioned rat, as is the increasing tendency to breathe just below the feedback threshold of 80 breaths/min (vertical black dotted lines). (C) Mean standard deviation of resting RR was used to assess reduction in RR variability. This index was reduced at Sessions 14, 15, and 20 in SRR conditioned vs. yoked rats, indicating more regular respiration. *p < 0.05 SRR conditioned vs. yoked, post-hoc Holm-Sidak comparisons.