FIGURE 6.
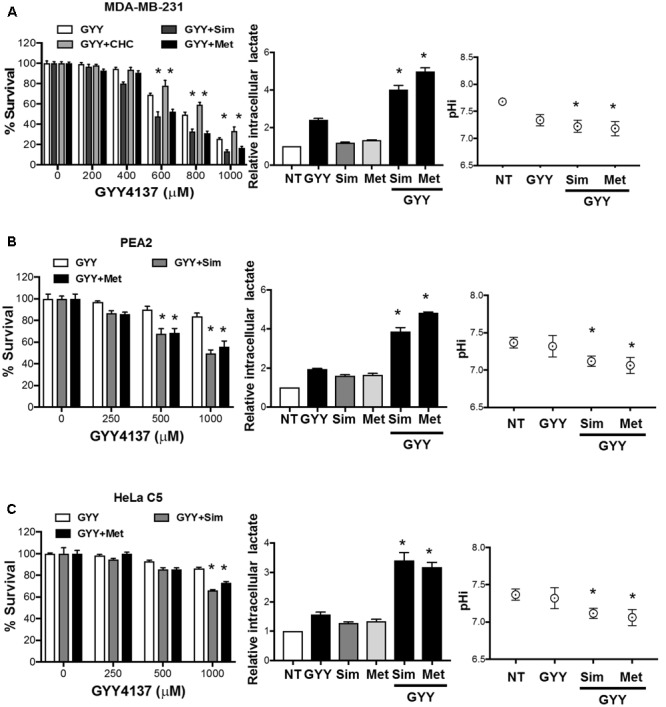
GYY4137 synergizes with simvastatin and metformin to impede aggressive cancers via lactate-induced intracellular hyper-acidification. (Left panel) (A) MDA-MB-231, (B) cisplatin-resistant PEA2 cells, (C) radio-resistant HeLa C5 were co-treated with GYY4137 (600 μM for MDA-MB-231 and 500 μM for HeLa C5 and PEA2) and either simvastatin (GYY4137+Sim, 1 μM) or CHC (GYY4137+CHC, 1 mM) or metformin (GYY4137+Met, 1 mM) for 3 days. Cell viability was examined using crystal violet assay. Combinatorial treatment of GYY4137 and simvastatin or metformin caused greater reduction in cell viability as compared to GYY4137 treatment alone. (Middle panel) Cells with single or combinatorial treatment of GYY4137 and simvastatin or metformin were harvested and lysed with 2% v/v perchloric acid solution. Lactate concentration was determined by lactate dehydrogenase enzymatic activity assay. Simvastatin or metformin treatment alone slightly increased lactate concentration of the cells. Combinatorial treatment of GYY4137 with simvastatin or metformin significantly increased lactate concentration. The increment was greater as compared to GYY4137 treatment alone. (Right panel) Intracellular acidification was determined by ratiometric fluorescence microplate assay. Combinatorial treatment of GYY4137 with simvastatin or metformin significantly decreased intracellular pH. The magnitude of decrease was greater as compared to GYY4137 treatment alone. All results show mean ± SD, n = 3. ∗P < 0.05.
