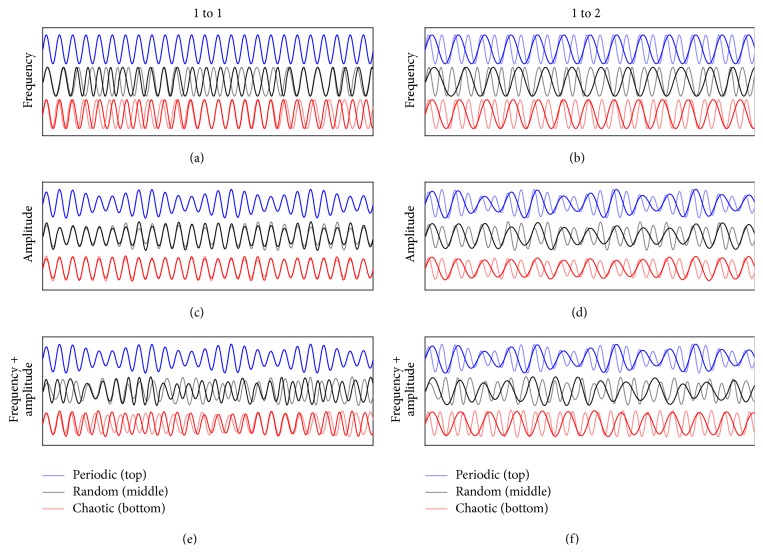
Figure 1.
Simulated sinusoidal signals used for analysis, which consist of periodic (top), chaotic (middle), and random (bottom) varying frequency (a, b), amplitudes (c, d), or both (e, f). Two of the seven different frequency ratios used in the analysis are represented: 1 : 1 (a, c, e) and 1 : 2 (b, d, f), where the lower frequency signal is denoted by a solid, dark line, and the higher frequency signal (1 Hz) is denoted by a solid, lighter line. The signals with a varying frequency all fluctuated between a minimum of 0.83∗fratio and a maximum of 1.23∗fratio seconds (a, b), whereas the signals with varying amplitude all fluctuated between a minimum of 0.5 and a maximum of 1 unit (c, d). Additionally, the signals with both varying frequency and amplitude shared these same characteristics (e, f).