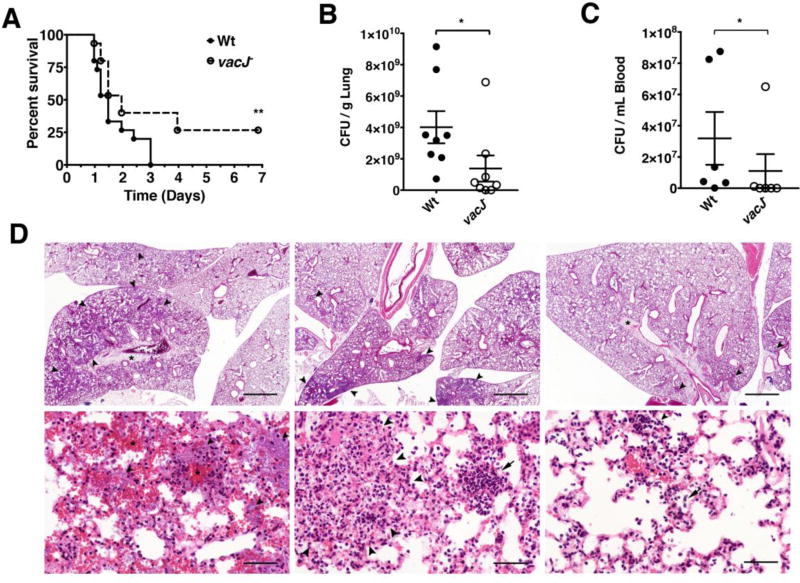
Figure 4. Effect of vacJ− mutation on P. aeruginosa virulence in murine pneumonia model.
Mice (n = 15 per group) were infected with P. aeruginosa wild-type or vacJ− (8.5×106 cfu / 30 µL PBS) intratracheally and observed for survival over a period of 7 d; * = P < 0.05 Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test (A). Mice (n = 8 per group) were infected with P. aeruginosa wild-type or vacJ− (4×106 cfu/ 30 µL) intratracheally and sacrificed 24 h post infection. Lungs were harvested (B) and blood collected (C) for bacterial enumeration. * = P < 0.05 two-tailed Mann-Whitney test. (D) Top panels (Scale bar = 1 mm). Left: Wt infected mouse 4, severity rank 1. Middle: vacJ− infected mouse 2, severity rank 5. Right: vacJ− infected mouse 1, severity rank 10. Alveoli (arrowheads) contain bacteria, inflammatory exudate, and hemorrhage. The interstitium is markedly expanded by edema (asterisks). Bottom panels (Scale bar = 50 µm). Left: Wt infected mouse 4, severity rank 1. The alveolar walls are coated by rod-shaped bacteria (arrowheads) and multifocal hemorrhage is present (asterisks). Middle: vacJ− infected mouse 2, severity rank 5. The pulmonary architecture is disrupted by a rare focus of necrosis (outlined by arrowheads) and alveoli are occasionally filled with neutrophils. Right: vacJ− infected mouse 1, severity rank 10. Small aggregates of (arrowhead) and scattered individual neutrophils (arrow) are present in alveoli.