Figure 4. Effects of V198E/P202L hERG on channel activation and deactivation.
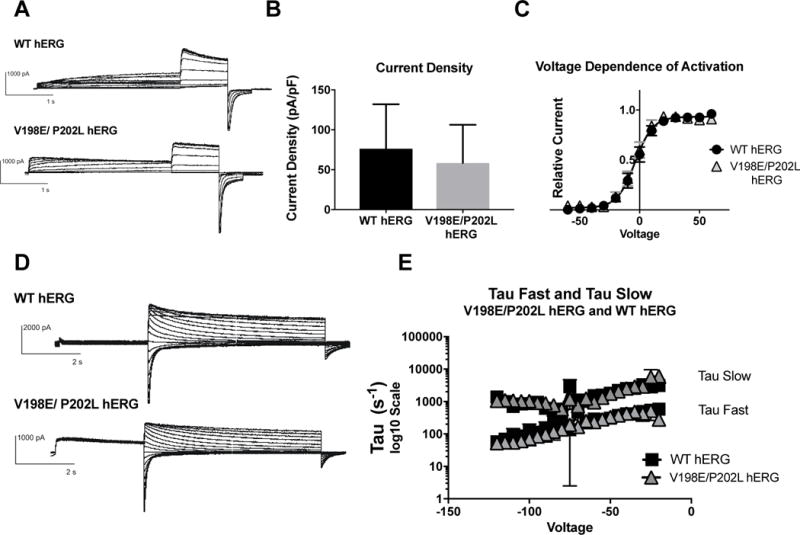
A) Whole cell patch clamp traces of WT hERG and V198E/P202L hERG activation. Voltage clamp protocol shown below trace. B) Current density for WT hERG and V198E/P202L hERG shown in graph form, normalized to cell capacitance. There are no significant differences in current density (n= 8 (WT) and 9 (V198E/P202L hERG)), although there is a trend towards decreased current density in the V198E/P202L hERG. C) Voltage Dependent Activation (VDA) for WT hERG and V198E/P202L hERG shows an identical curve. D) Whole cell patch clamp traces of WT hERG and V198E/P202L hERG deactivation. Voltage clamp protocol shown below trace. N= 2 (WT hERG) and 3 (V198E/P202L hERG). E) Graph of WT and V198E/P202L hERG Slow Tau deactivation and Fast Tau deactivation on a Log10 scale y-axis. There are no differences between WT hERG and V198E/P202L hERG. The V198E/P202L variants do not affect hERG channel deactivation kinetics.
