Figure 7. Impact of D219V mutation on hERG channel activation.
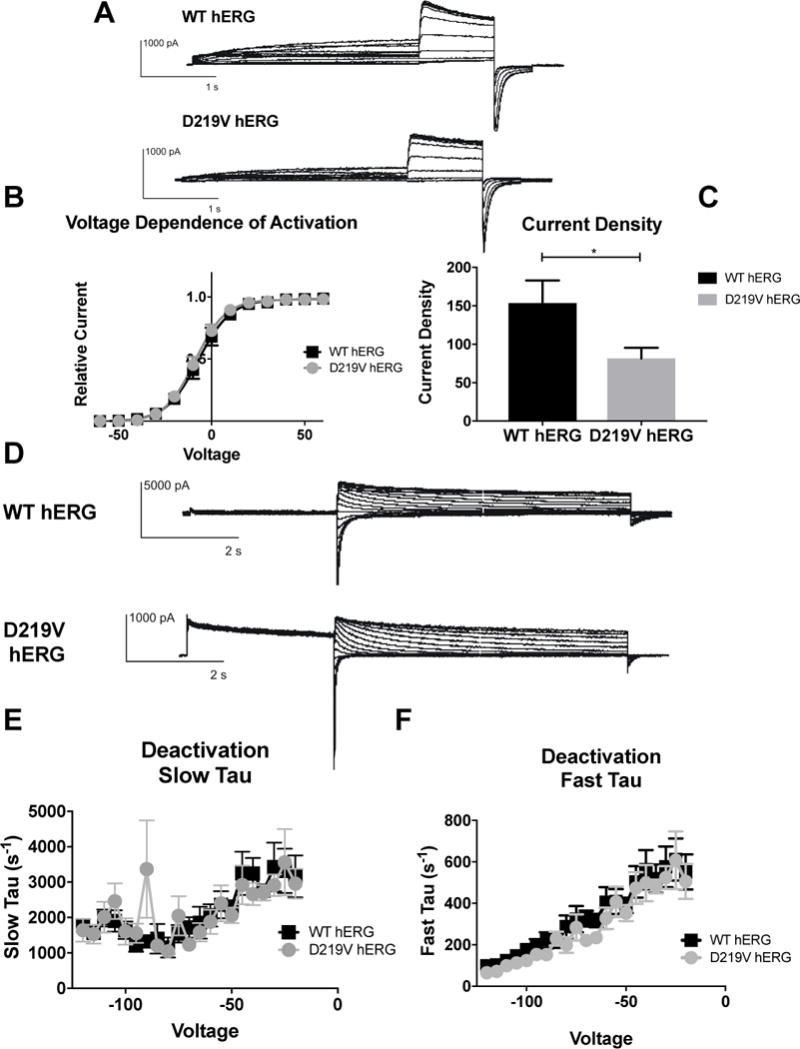
A) Whole cell patch clamp traces of WT hERG and C-terminal myc hERG activation. Voltage clamp protocol shown below trace. B) Current density for WT hERG and D219V hERG shown in graph form, normalized to cell capacitance. There are significant differences in current density. D219V hERG has a decreased current density (n= 12 (WT) and 13 (D219V hERG), p=0.0326). C) Voltage Dependent Activation (VDA) shown for WT hERG and D219V hERG. The VDA curve is similar for both D219V hERG and WT hERG, although D219V hERG is slightly left shifted (WT-hERG V1/2= −7.182 ± 0.1371 and D219V hERG V1/2 = −8.886 ± 0.143). D) Whole cell patch clamp traces of WT hERG and D219V hERG activation. N= 12 (WT hERG) and 9 (D219V hERG). E) Graph shows WT and D219V hERG Slow Tau deactivation. There are no significant differences between WT and D219V hERG. F) Graphical representation of Fast Tau deactivation. There are no differences between WT hERG and D219V hERG. The D219V mutation does not affect hERG channel deactivation kinetics.
