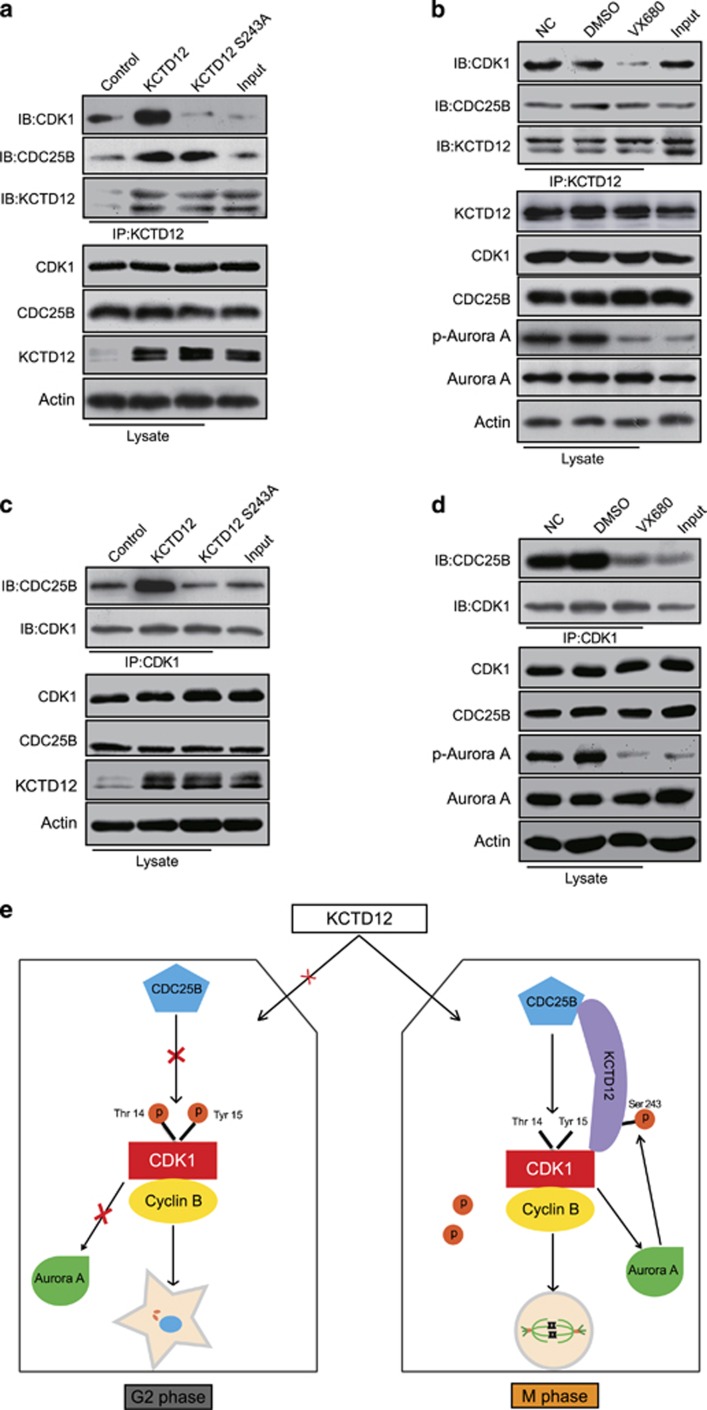
Figure 7.
KCTD12 interacts with CDC25B and CDK1 to form a positive feedback loop and facilitate the G2/M transition. (a, b) KCTD12 S243 phosphorylation was necessary for its interaction with CDK1 but not CDC25B. The HeLa cells transfected with KCTD12 wild-type plasmid or S243A mutant plasmid (1 μg, 24 h) were used to perform the immunoprecipitation assays (a), and the cells treated with VX-680 (0.5 μM, 24 h) were used to determine the impact of Aurora A on the interaction of KCTD12 and CDC25B or CDK1 (b). (c) The HeLa cells were transfected with wild type KCTD12- or S243A mutant-expressing plasmid (1 μg, 24 h), and CDC25B expression was analyzed in the CDK1 immunoprecipitates by immunoblotting. Expression levels of CDK1, CDC25B, KCTD12 and Actin were also determined in the whole cell lysates. The cells used for immunoprecipitation were synchronized to M phase. (d) The interaction of CDC25B and CDK1 in the HeLa cells treated with DMSO or VX-680 (0.5 μM, 24 h) were assessed by immunoprecipitation and western blotting. Cells were synchronized to M phase for immunoprecipitation. (e) Schematic diagram summarizing how the KCTD12-CDC25B-CDK1-Aurora A positive-feedback loop facilitates cell entry into mitosis.