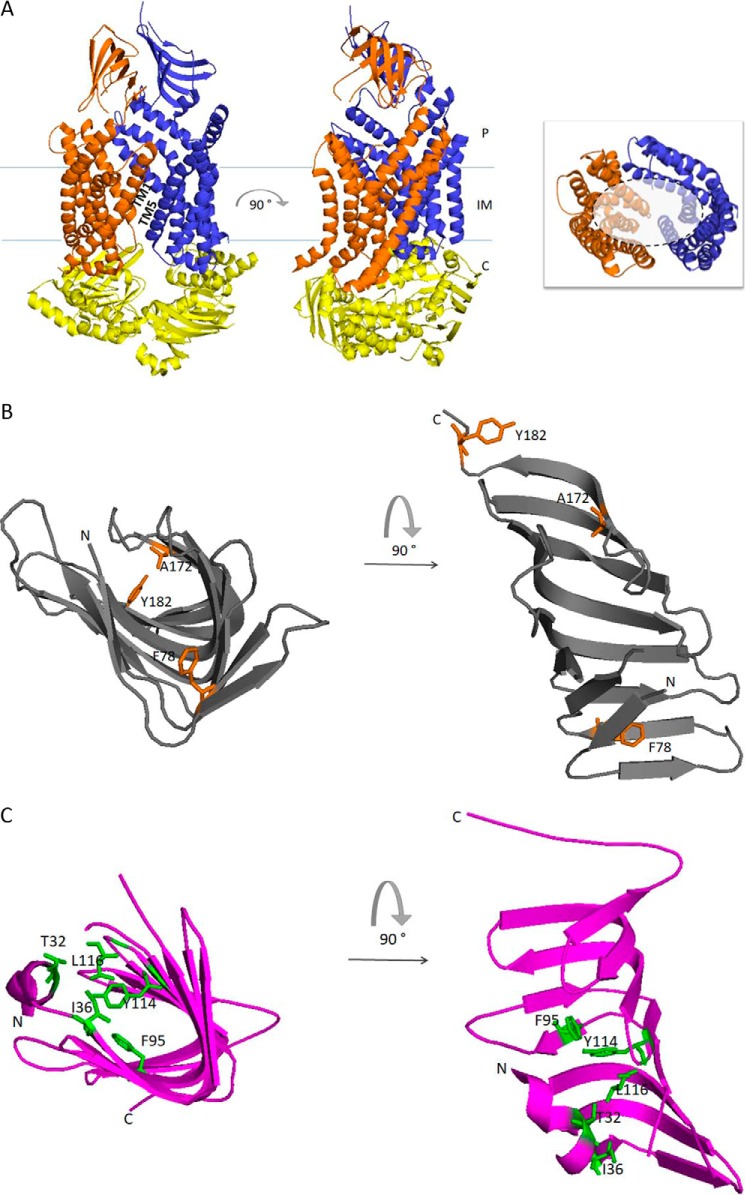
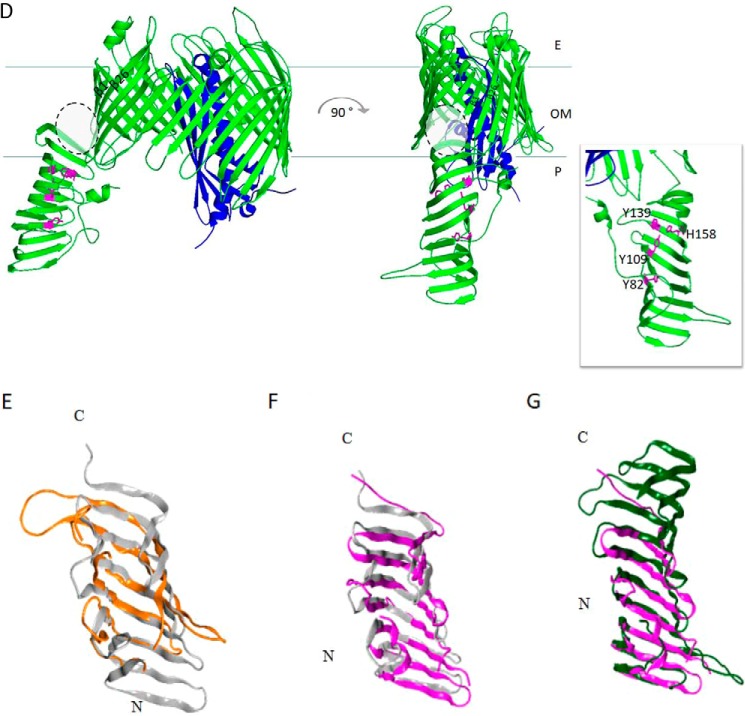
Figure 2.
Graphic representation of the crystal structures of the seven Lpt proteins and structural comparisons. A, LptB2FG complex from P. aeruginosa (Protein Data Bank (PDB) 5X5Y). LptB, LptF and LptG are represented in yellow, orange, and blue, respectively. The 12 TM helices of LptF–G bent outwards, creating a V-shaped central cavity at the membrane–periplasm interface, which would function as an LPS-binding pocket. TM1 of LptF with TM5 of LptG and TM1 of LptG with TM5 of LptF constitute the lateral gates that would allow the entry of LPS into the central cavity of the transporter (58). Inset, top view of the V-shaped central cavity highlighted by a dotted circle; for clarity, periplasmic β-jellyroll-like domains of LptF–G and LptB dimer have been removed. B, LptC from E. coli (gray, PDB 3M2Y). Residues in LptC involved in LPS binding as assessed by photo-crosslinking experiments are depicted in orange (59). Thr-47 residue is not shown because the electron density of this region is absent in the structure. C, LptA from E. coli (magenta, PDB 2R19). Residues in LptA involved in LPS binding as assessed by photo-crosslinking experiments are depicted in green (59). D, LptDE complex from K. pneumoniae (PDB 5IV9). LptD is colored green, and LptE, inserted in the LptD lumen, is colored blue. During transport, lipid A moiety of LPS is bound by the N-terminal domain of LptD and inserted directly into the membrane through an intramembrane hole (highlighted by gray dotted circle). The saccharide portion of LPS passes through the lumenal gate formed by β-strands 1 and 26 of the C-terminal domain of LptD. Inset, residues in the LptD N-terminal domain involved in LPS binding have been experimentally detected in S. enterica serovar Typhimurium (79), and the corresponding residues identified by structural alignment with the LptD homologue from K. pneumoniae are depicted in magenta. The model structures were generated with PyMOL using the corresponding PDB files. E–G, the β-jellyroll domain of LptF (orange, PDB 5X5Y) superimposed on LptC (gray, PDB 3M2Y) (E); LptC (gray, PDB 3M2Y) superimposed on LptA (magenta, PDB 2R19) (F); and LptA (magenta, PDB 2R19) superimposed on the N-terminal β-jellyroll domain of LptD (green, PDB 5IV9) (G). Superimpositions were obtained manually using the Maestro software. E, extra-cytoplasmic milieu; P, periplasm; C, cytoplasm.