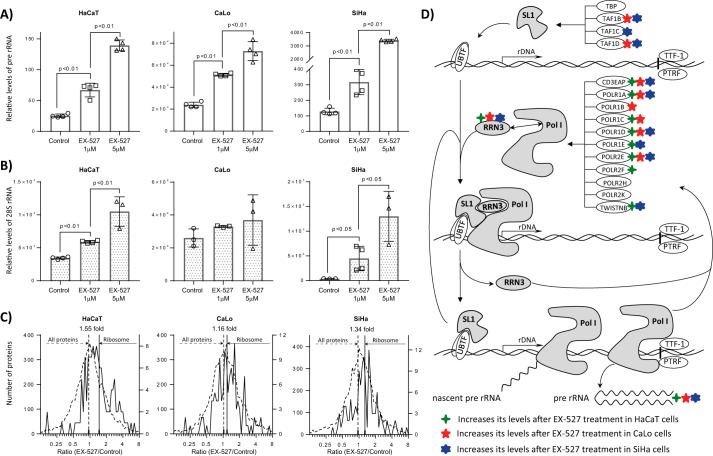
Figure 7.
The chemical inhibition of SIRT1 by treating cells with EX-527 increases the levels of pre-rRNA and the mature 28S rRNA in a dose-dependent manner. HaCaT, CaLo, and SiHa cells were treated with vehicle, 1 μm EX-527, and 5 μm EX-527 for 24 h, and the level of pre-rRNA (A) and 28S rRNA (B) were estimated by RT-qPCR relative to actin mRNA levels. Error bars represent S.D. C, the levels of the proteic components of the ribosomes were analyzed as the ratio of the protein intensities between cells treated with 1 μm EX-527 and control. The ratio of protein intensities was distributed on a log2 scale. Ribosomal proteins are represented in continuous lines, and all quantified proteins are shown in discontinuous lines. The means of all ratios are presented as continuous vertical lines for ribosomal proteins and discontinuous lines for all proteins. D, schematic representation of the synthesis of pre-rRNA and proteins involved in this process. SIRT1 inhibition increases the levels of proteins involved in the synthesis of pre-rRNA. Elements of SL1 complex required for the formation of the preinitiation complex were up-regulated in CaLo and SiHa cells. Most of the components specific for the Pol I complex as well as the protein RRN3 required for the activation of Pol I and for the interaction with SL1 complex at the transcription start site were up-regulated in the three cells lines analyzed. UBTF, nucleolar transcription factor 1; TTF-1, transcription terminator factor 1; PTRF, polymerase I and transcript release factor; TBP, TATA-binding protein; TWISTNB, TWIST neighbor.