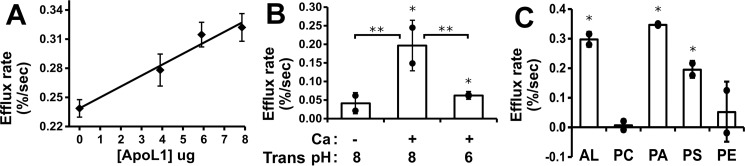
Figure 6.
Characterization of ApoL1-dependent potassium permeability. A, ApoL1 concentration dependence. Efflux assays were performed with a range of ApoL1 concentration in the initial reaction mix at pH 6, and then efflux was assayed at pH 7.5. To eliminate the possibility of buffer or detergent effects, the total volume of S200 buffer solution added to the reaction was held constant. Data points represent the mean, and error bars represent S.E.; n = 2 for each data point. B, calcium and trans pH dependence of activity. Assays were performed with and without ApoL1, with initial reaction at pH 6 and efflux at pH 7.5, in the absence or presence of 2 mm calcium using vesicles with the internal compartment buffered at 8 (left and center) or in the presence of 2 mm calcium using vesicles with the internal pH buffered at either 8 or 6 (center and right). C, lipid dependence of potassium permease activity. ApoL1 or control buffer was mixed at pH 6.0 with vesicles comprised of various combinations of purified lipids and assayed for CI1 dependent efflux at pH 7.5. Lipid mixtures are labeled as in Fig. 4E. B and C, individual data points show the ApoL1-dependent rate above the no-protein control rates for each condition. Columns represent the mean, and error bars represent standard deviation; n = 2 for each data point. *, p < 0.05 compared with the no-protein control rate; **, p < 0.05 for the pairwise comparisons indicated by brackets; significance was determined using ANOVA.