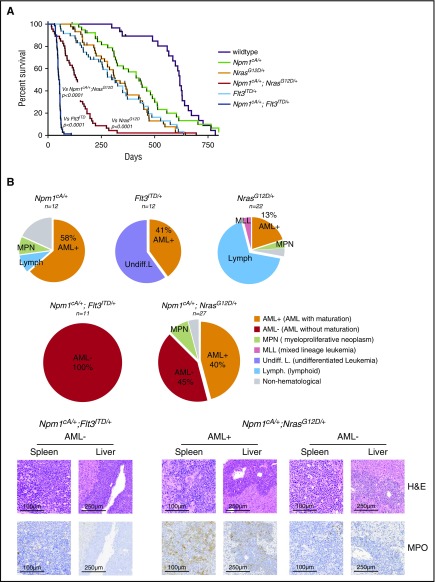
Figure 3.
Npm1cAand NrasG12Dcooperate to drive high-penetrance AML. (A) Kaplan- Meier survival curves of wild-type (n = 23), Npm1cA/+ (n = 34), NrasG12D/+ (n = 40), Flt3ITD/+ (n = 39), Npm1cA/+;NrasG12D/+ (n = 46), and Npm1cA/+;Flt3ITD+/ (n = 40). Double mutant (Npm1cA/+;NrasG12D/+ and Npm1cA/+;Flt3ITD/+) mice had a significantly shortened survival when compared with single mutants, and Npm1cA/+;Flt3ITD had significantly shorter survival than Npm1cA/+;NrasG12D/+ mice. (B) Results of independent histopathological analysis of aged moribund mice. Incidence of AML in compound Npm1cA/+;NrasG12D/+ and Npm1cA/+;Flt3ITD/+ mice is increased in comparison with Npm1cA/+, NrasG12D/+, and Flt3ITD/+ mice. Examples of complete effacement of splenic tissue and infiltration of myeloid blast cells in liver tissue from Npm1cA/+;NrasG12D/+ and Npm1cA/+;Flt3ITD+/ AMLs are presented. Reduced myeloperoxidase (MPO) staining in diseased tissues is observed in samples categorized as AML without maturation (AML−) in comparison with those categorized as AML with maturation (AML+). H&E, haematoxylin and eosin.