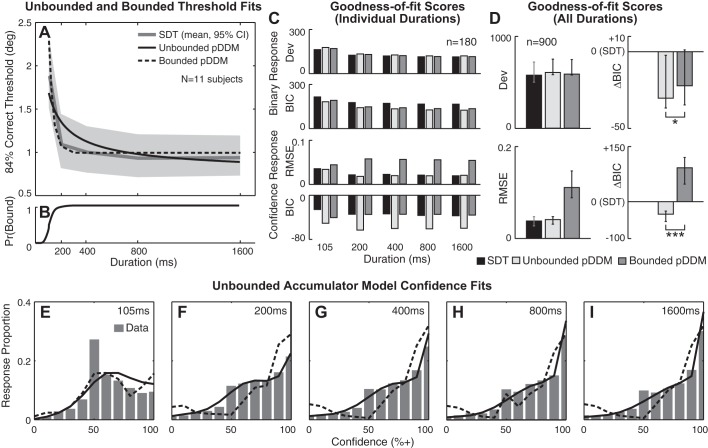
Fig. 4.
Model comparisons: unbounded and bounded pure accumulator models (pDDM). A: binary choice threshold estimates as a function of stimulus duration. Unbounded pDDM, bounded pDDM, and signal detection theory (SDT) threshold predictions were averaged across 11 subjects. Gray shading shows 95% CI for SDT estimates. B: probability of hitting a bound as a function of stimulus duration in bounded pDDM. C: mean goodness-of-fit scores at individual stimulus duration for binary responses (top) and confidence responses (bottom). D: marginal goodness-of-fit scores across all durations for binary responses (top) and confidence responses (bottom). Horizontal bars: *positive evidence (ΔBICBounded − Unbounded > 2), ***very strong support (ΔBICBounded − Unbounded > 10) for unbounded pDDM. Error bars show lower and upper quartiles. E–I: confidence histograms aggregated across all stimulus levels for 11 subjects. Solid black curves, unbounded pDDM; dashed black curves, bounded pDDM.