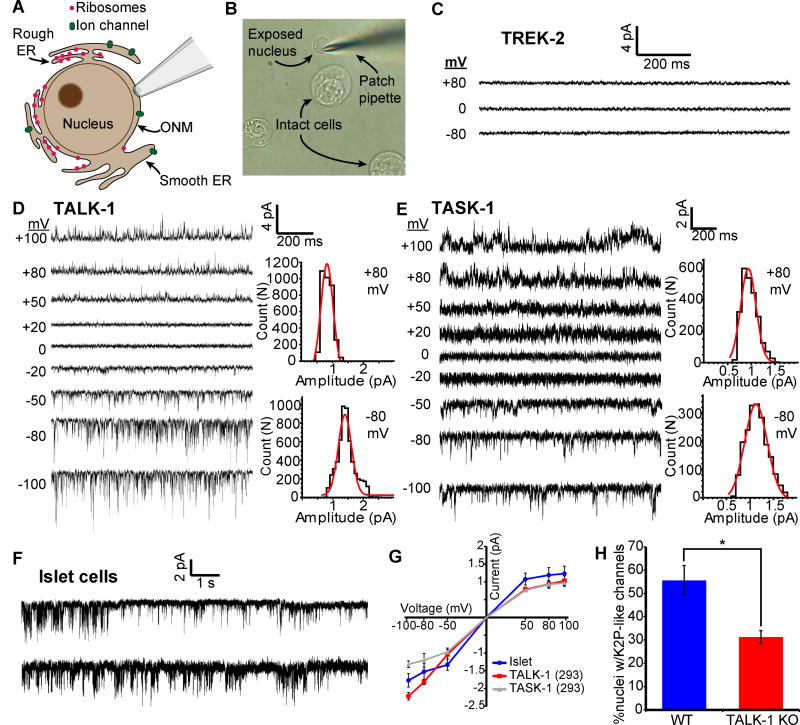
Figure 5. Functional TALK-1 and TASK-1 channels are present in the ER membrane.
(A) Nuclear patch clamp of the outer nuclear membrane (ONM) permits detection of ER ion channels. (B) Representative image of isolated mouse islet nuclei with patch pipette positioned on nucleus. (C) Recordings obtained from the nucleus of a TREK-2-expressing HEK293 cell (representative of 5 nuclei). (D) Current trace obtained from the nucleus of a TALK-1 expressing HEK293 cell. Representative current amplitude histograms at right (representative of 8 nuclei). (E) As in D, but recorded from the nucleus of a TASK-1 expressing cell (representative of 7 nuclei). (F) Representative current traces obtained from WT mouse nuclei; patches held at −50 mV (representative of 42 nuclei) (G) Single-channel current-voltage relationships from nucleus recordings obtained from TALK-1- (N = 8) and TASK-1- (N = 7) expressing HEK293 cells and WT islet-cells (N = 42). (H) Percent of nuclei with K2P-channel-like channel activity detected in WT and TALK-1 KO β-cells (N = 42 nuclei; 4 mice per genotype). Statistical significance was determined by Student’s t-test; *P<0.05.